 There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
Ofcom has a duty to ensure spectrum isn’t wasted and as a consequence of the auction will end up driving revenue for the Government. Previously, and famously they did very well when they auctioned the 3G licenses, raising £21bn for the Treasury.
They recently auctioned some GSM spectrum and that only raised £3.8m, but it was much less than the 3G lot with many more restrictions.
Under its new face, and following EU directives, Ofcom likes to offer technology neutral licenses, which means the licensee can use the spectrum for whatever they want – as long as they meet the radio restrictions on that band (power, spectral masks, etc). They hope this will stimulate innovative services which is good for the economy.
There’s a lot of interest in the spectrum, as it could be used for lots of services including 3G and WiMAX, but that’s where the problems start.
Possible European Interference
There are various blocks of spectrum which are coordinated at a European level and each EU country uses the spectrum for the same things. That’s pretty much what happens for GSM and 3G, as well as some TV and radio bands.
It’s all organised by CEPT (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications) and the Radio Spectrum Committee (RSC), CEPT is represented by 47 countries and the RSC by 25 EU states. They ensure that radio usage is coordinated. Unfortunately radio waves don’t abide by national borders, so it would be no good if one country was using spectrum for say TV and another for radio as they’d interfere with each other.

Though the UK is an island, interference issues are quite common, especially in the south east with France and the north east with the Dutch and even the Nordic countries. The west has to worry about Ireland (and of course Northern Ireland abides by UK policy).
These particular bands are already allocated for 3G, 10MHz in 2010 – 2020 MHz, is already designed for license-exempt self-provided, self-coordinated IMT-2000 use. In the UK none of the 3G networks have actually utilised it, though in other parts of Europe it has been used for this purpose.
2500 – 2690 MHz is currently mainly used for video broadcast systems, all licensees have been given notice to vacate by 31st December 2006. This is a significant amount of spectrum (190MHz) which is greater than is currently allocated to the whole of 3G use (140MHz). It was reserved for a “new” entrant if the current 5th 3G operator failed or for existing 3G expansion.
Ofcom’s suggestions summarised
Ofcom are currently holding UK consultations to see what stakeholders think should happen. They are proposing the following: –
2500-2690 MHz Packaged on the basis of blocks of 5 MHz as lots of paired spectrum (2×5 MHz, 120 MHz duplex spacing) and unpaired spectrum (5 MHz), with the eventual amount of lots in each category to be determined in the auction. The reference point is as per the CEPT band plan: 14 lots of paired channels (14x2x5 MHz with uplink in 2500-2570 MHz and downlink in 2620-2690 MHz) and 9 lots of unpaired channels (9×5 MHz in 2570-2615 MHz).
One guard channel will be necessary at adjacencies between paired and unpaired spectrum, at 2615-2620 MHz, and possibly another in the top part of the band.
There is a possibility to allow paired lots to be converted into the equivalent of two unpaired lots in the event that demand for unpaired lots exceeds that for paired lots at a given lot price.
Each bidder should receive contiguous lots in each category, except potentially one assignment of unpaired spectrum which could need to be split into two blocks of contiguous lots.
2010-2025 MHz Package for award as a single 15 MHz lot.
2290-2302 MHz Package for award as a single 10 MHz lot and retain 2300-2302 MHz for possible inclusion as part of a future award together with 2302-2310 MHz.
What might the response be?
The consultation will close in March 2007 and it’s likely the 3G operators will be extremely vocal in their claim to this spectrum, as they paid so much for their original licenses.
Once Ofcom digest the responses, they’ll then have to argue the case at the European level to ensure it can be licensed off in a technology neutral manner without upsetting our neighbours, however getting agreement from at least 47 countries tends to be a time consuming process.
Luckily CEPT are already discussing the issues and are expecting to make a statement in July next year. RSC will follow shortly after.
Although there’s no guarantee that discussions will go in Ofcom’s favour, they are hoping an award process can start in the Autumn of 2007, though it may well be delayed until 2008.
Potential Cash
With 16 national licenses available, there’s a fair amount of cash the government can expect to raise. Even if Ofcom set the minimum price at £50,000 then that’s £800,000 – they are likely to reach much higher values, although not the silly pricing that the original 3G licenses fetched.
Ofcom
CEPT (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications)
Radio Spectrum Committee (RSC)
 Although most of the information can be had elsewhere, it’s useful to have a single source where everything’s in one place. Forgotten how to reset your iPod? It’s in the Missing Manual.
Although most of the information can be had elsewhere, it’s useful to have a single source where everything’s in one place. Forgotten how to reset your iPod? It’s in the Missing Manual. Currently Vodafone have a bigger network than Orange, so Orange would gain more than Vodafone from the deal, but in future it means that new cell sites will be used by both operators.
Currently Vodafone have a bigger network than Orange, so Orange would gain more than Vodafone from the deal, but in future it means that new cell sites will be used by both operators. Why the rush to build?
Why the rush to build? Though city centres might have a demand for 3G (for data services, no one cares about 3G voice – a voice call sounds the same whether it’s 3G or GSM), as you leave dense urban areas the appeal of 3G is less. Well maybe not less, but there are less people to use it and less of a reason for the networks to install 3G infrastructure and sites.
Though city centres might have a demand for 3G (for data services, no one cares about 3G voice – a voice call sounds the same whether it’s 3G or GSM), as you leave dense urban areas the appeal of 3G is less. Well maybe not less, but there are less people to use it and less of a reason for the networks to install 3G infrastructure and sites. There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
 It’s coming up to Xmas and everyone’s making Skype accessories. Belkin are no exception and have joined the crowd to release a Skype phone, in BLACK.
It’s coming up to Xmas and everyone’s making Skype accessories. Belkin are no exception and have joined the crowd to release a Skype phone, in BLACK. If you’ve got credit you can make normal calls to the PSTN (i.e.ordinary phones), but you have to type the telephone number in international format (i.e. putting +44 infront of the number and dropping the leading zero). Unless you’ve got a SkypeIn number, the called phone will show “Number Unavailable” when you call.
If you’ve got credit you can make normal calls to the PSTN (i.e.ordinary phones), but you have to type the telephone number in international format (i.e. putting +44 infront of the number and dropping the leading zero). Unless you’ve got a SkypeIn number, the called phone will show “Number Unavailable” when you call. Phone Set-up
Phone Set-up It’s not perfect
It’s not perfect Recently while travelling on an SAS flight, I had the pleasure of trying out the Connexion by Boeing service, which is an Internet service offered on long haul services.
Recently while travelling on an SAS flight, I had the pleasure of trying out the Connexion by Boeing service, which is an Internet service offered on long haul services.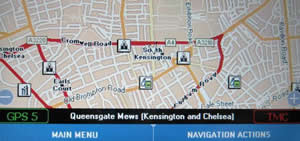 ViaMichelin is the part of the Michelin group that designs, develops and markets digital travel assistance products. They already have a successful Website that uses information from the Michelin Guide allowing visitors to plan their travel and routes utilising the Guide info.
ViaMichelin is the part of the Michelin group that designs, develops and markets digital travel assistance products. They already have a successful Website that uses information from the Michelin Guide allowing visitors to plan their travel and routes utilising the Guide info. Why get a X-980T?
Why get a X-980T? There’s also a speed camera database for the UK (which isn’t actually available yet, but will be in late October) and other countries. Again it’s included in the price (as are updates).
There’s also a speed camera database for the UK (which isn’t actually available yet, but will be in late October) and other countries. Again it’s included in the price (as are updates). Overall Verdict
Overall Verdict THUS, the communications provider that owns the Demon brand has announced it has become the preferred supplier for HSBC in the UK. The contract is expected to be around £50m plus over 5 years.
THUS, the communications provider that owns the Demon brand has announced it has become the preferred supplier for HSBC in the UK. The contract is expected to be around £50m plus over 5 years. THUS also recently acquired Your Comms (a business telco based in the North of England) and Legend, a smallish ISP with a portfolio of VoIP products. Other acquisitions must be on their mind.
THUS also recently acquired Your Comms (a business telco based in the North of England) and Legend, a smallish ISP with a portfolio of VoIP products. Other acquisitions must be on their mind. A Brazilian company has forged a software bridge between Asterisk and Skype.
A Brazilian company has forged a software bridge between Asterisk and Skype. One feature that has been missing is Skype integration (the next version of Asterisk v1.4 supports GoogleTalk using Google’s libjingle library). A Brazilian company has now changed that, with their ChanSkype site.
One feature that has been missing is Skype integration (the next version of Asterisk v1.4 supports GoogleTalk using Google’s libjingle library). A Brazilian company has now changed that, with their ChanSkype site. CSR, a chipset design lab in Cambridge that specialises in radio, has released a voice over WiFi design (UniVox) which a bill of materials of around £11.00.
CSR, a chipset design lab in Cambridge that specialises in radio, has released a voice over WiFi design (UniVox) which a bill of materials of around £11.00. Both SIP (version 2) and IAX2 (Inter Asterisk Protocol v2) are supported. IAX is useful in NAT environments as it can traverse NAT without any special software, while SIP can be a complete headache.
Both SIP (version 2) and IAX2 (Inter Asterisk Protocol v2) are supported. IAX is useful in NAT environments as it can traverse NAT without any special software, while SIP can be a complete headache. Apple has for once pre-announced a new product, codenamed iTV (which is unlikely to be the final name as they’d get sued in the UK for a start).
Apple has for once pre-announced a new product, codenamed iTV (which is unlikely to be the final name as they’d get sued in the UK for a start).