 How do ‘Normal’ phones work?
How do ‘Normal’ phones work?
Traditional telephony networks aka POTS (Plain Old TelephonySystems) are based on a network fabric using TDM (Time DivisionMultiplexing), a technology that’s been around for a longtime.
How does a POTS call work? When a call is established between two phone users, a “virtual circuit” is established between them and a certain amount of bandwidth reserved across that circuit (usually 64Kb/s). That bandwidth is reserved for the lifetime of the call, even if no-one is speaking. As the connection is synchronous, ie. when someone talks, the voice is sent across the network in the sequence that it was said. This occurs until the end of the call.
It’s different with VoIP
With the move to VoIP, voice first gets digitised, turned into small packets, which are then encoded into IP packets, in turn sent across an IP network. The packetisation actually adds overhead (takes longer and adds to the size), leading to VoIP sometimes utilising more network bandwidth than traditional telephony methods. Of course this can be mitigated by using modern CoDecs (the digitisers) which use more compression than traditional telephony. Unfortunately the more compression used, the lower the call quality. In a mobile network, voice is encoded at 13Kb/s (which increases to 20Kb/s+ when packetised – as an example of the overhead). People are used to this reduced quality, despite it being noticeably different from a phone call using a fixed-line.
![]() Using VoIP over the Internet is a hit and miss thing. We know the Internet is fantastic at coping with problems – if there are network errors, the data is re-routed around the black-spots, and when the error goes or traffic gets congested, it just re-routes the data somewhere else. It’s best to think of the Internet as a loose collection of around 30,000+ networks that happen to interconnect at various places.
Using VoIP over the Internet is a hit and miss thing. We know the Internet is fantastic at coping with problems – if there are network errors, the data is re-routed around the black-spots, and when the error goes or traffic gets congested, it just re-routes the data somewhere else. It’s best to think of the Internet as a loose collection of around 30,000+ networks that happen to interconnect at various places.
Where the re-routing works for general Internet traffic, it’s terrible for VoIP as there’s no guarantee that the VoIP data will arrive in an orderly fashion i.e. the first bit of traffic may go one way, then second another and the third another route completely. Each route will have be working at different speeds, so the 3rd piece of VoIP data may actually arrive at the destination first – imagine the third word of the conversation arriving before the first.
Packets arriving in a different order is expected on the Internet and it was designed with this in mind. IP can reassemble the data and put it all back in the right order, but to do so requires large buffers i.e long delays. Unfortunately for VoIP, delay not is something you want as that’s when calls break-up or crack and pop.
In the trade, the packets arriving at different times (relative to a clock signal i.e. like a metronome) is called Jitter.
 VoIP in an ideal world
VoIP in an ideal world
There are ways to get around this. Such as new technologies like IP/MPLS (IP/Multi Protocol Label Switching) which is a way of ensuring all traffic between two points goes the same way (with back-up routes, in case the primary one fails). It also allows for Quality of Service (QoS) metrics, so VoIP traffic can be prioritised over say Web traffic, minimising Jitter.
Many telecoms companies now run IP networks utilising IP/MPLS, but as they still interconnect over other, public connection points any quality metrics are lost. So as long as all your IP services come from the same supplier, you’re unlikely to be able to maintain QoS.
When does VoIP make sense/when not
VoIP does gives increased flexibility and anyone with a multi-site operation should consider it. If they’re currently paying bills to a telecoms company to transfer calls between sites, the use of VoIP is generally a no brainer, as it give a rapid payback for the added VoIP equipment required.
When to think twice about VoIP
Single site businesses, should be wary. Installing VoIP can consume significant resources when converting from a traditional system in particular using VoIP may require extensive reworking of an internal LAN – you don’t want your phone calls to stop when someone transfers a large file between their PC and the server.
It may be better to look at other options such as Carrier Pre Select (CPS) or Wholesale Line Rental (WLR) or simply another telecom’s provider whose rates are better.
 Security implications and therefore costs are a significant issue. The increase in network traffic that VoIP can bring can have other cost implications, such as ensuring firewalls are “chunky” enough to support the VoIP traffic.
Security implications and therefore costs are a significant issue. The increase in network traffic that VoIP can bring can have other cost implications, such as ensuring firewalls are “chunky” enough to support the VoIP traffic.
One area that isn’t often spoken about, but we feel is a big weakness of VoIP is the potential of all phone calls in and out of the site that are carried over VoIP being lost to a DoS (Denial of Service) attack. Protecting against attacks can be difficult, as the attacks may just look like remote workers trying to establish VoIP calls into the network.
Conclusion
VoIP isn’t a panacea. While it can offer savings and great flexibility, the choice shouldn’t be automatic. Look at the whole picture and work out if there really are savings to be made. If there’s no ROI (Return on Investment), then VoIP is an expensive new toy.
 Looking for new sources of revenue beyond their Internet telephony service, Skype have announced a deal with Warner Music Group to flog ring tones and artist images.
Looking for new sources of revenue beyond their Internet telephony service, Skype have announced a deal with Warner Music Group to flog ring tones and artist images. “We are excited that more than 70m Skype users around the world will now have the ability to enjoy content from Warner Music artists,” said Alex Zubillaga, executive vice-president in charge of digital strategy and business development at Warner Music (that’s some job title – we wonder if he meets people saying, “Hi, I’m Alex Zubillaga, EVPICODSABD at Warners?”)
“We are excited that more than 70m Skype users around the world will now have the ability to enjoy content from Warner Music artists,” said Alex Zubillaga, executive vice-president in charge of digital strategy and business development at Warner Music (that’s some job title – we wonder if he meets people saying, “Hi, I’m Alex Zubillaga, EVPICODSABD at Warners?”) Ringtone sales have proved a surprise hit for mobile operators and content providers, coining in an astonishing $4bn in worldwide sales in 2004 – around 10 per cent of the $32.2bn worldwide music market.
Ringtone sales have proved a surprise hit for mobile operators and content providers, coining in an astonishing $4bn in worldwide sales in 2004 – around 10 per cent of the $32.2bn worldwide music market. BT’s dominance of the UK home telephone is coming under fresh pressure as the phone call market becomes the most liberal in Europe. Previously, their pricing levels have had to be agreed in advance with the UK regulator Ofcom, but with it understood that this is going to be lifted soon, price cuts are expected.
BT’s dominance of the UK home telephone is coming under fresh pressure as the phone call market becomes the most liberal in Europe. Previously, their pricing levels have had to be agreed in advance with the UK regulator Ofcom, but with it understood that this is going to be lifted soon, price cuts are expected. Technical-savvy Skype callers have for a long time taken advantage of VoIP calling to obtain free or cheap calls.
Technical-savvy Skype callers have for a long time taken advantage of VoIP calling to obtain free or cheap calls. It’s been a long time coming, but Dutch enormo-corp Philips are looking set to finally roll out their innovative Wi-Fi-enabled VoIP telephone, the VP-5500.
It’s been a long time coming, but Dutch enormo-corp Philips are looking set to finally roll out their innovative Wi-Fi-enabled VoIP telephone, the VP-5500. Announced way back in Sept 2005, the VoIP phone comes with a VGA camera that rotates up to 240 degrees, letting users check out their look on the built-in, high-resolution LCD display before committing a potential videocall fashion catastrophe.
Announced way back in Sept 2005, the VoIP phone comes with a VGA camera that rotates up to 240 degrees, letting users check out their look on the built-in, high-resolution LCD display before committing a potential videocall fashion catastrophe. Built around established standards-based technologies like Wi-Fi and Linux, the VP5500 can be upgraded wirelessly, opening the door to future upgrades – giving operators the chance to add value-added services as the becmoe available.
Built around established standards-based technologies like Wi-Fi and Linux, the VP5500 can be upgraded wirelessly, opening the door to future upgrades – giving operators the chance to add value-added services as the becmoe available. To be honest, we’re still a little unsure about video calling.
To be honest, we’re still a little unsure about video calling. No idea if we’re ever going to see it turning up in Blighty any time soon, but we love this crazy new Sony VN-CX1 USB optical mouse-phone.
No idea if we’re ever going to see it turning up in Blighty any time soon, but we love this crazy new Sony VN-CX1 USB optical mouse-phone. The clever stuff happens when a call comes in.
The clever stuff happens when a call comes in. A potential problem might arise if you wanted to use the mouse when you’re on a call, but we think you can just switch to speakerphone mode. Or maybe not (the translated press announcement goes on about ‘knitting machines’ so it’s a bit vague).
A potential problem might arise if you wanted to use the mouse when you’re on a call, but we think you can just switch to speakerphone mode. Or maybe not (the translated press announcement goes on about ‘knitting machines’ so it’s a bit vague). Although the VN-CX1 doesn’t look like the most comfortable mouse we’ve ever seen, it’s small and light enough (45.5 × 23.9 × 89.2 mm, 67gms) and certainly looks a fun product.
Although the VN-CX1 doesn’t look like the most comfortable mouse we’ve ever seen, it’s small and light enough (45.5 × 23.9 × 89.2 mm, 67gms) and certainly looks a fun product. D-Link’s new Skype USB phone adapter (DPH-50U) is a neat widget that lets users make and receive Skype calls on their existing corded DECT or cordless phone, without the need to have a pesky ‘call centre’ headset stuck on their head.
D-Link’s new Skype USB phone adapter (DPH-50U) is a neat widget that lets users make and receive Skype calls on their existing corded DECT or cordless phone, without the need to have a pesky ‘call centre’ headset stuck on their head.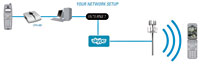 The concept seems a winner to us – by using your existing telephone you should enjoy better sound quality than a cheapo headset, and D-Link claim that you’ll be able to use your phone’s built-in features such as speed dial, redial, mute and caller ID2 for both Skype and landline calls.
The concept seems a winner to us – by using your existing telephone you should enjoy better sound quality than a cheapo headset, and D-Link claim that you’ll be able to use your phone’s built-in features such as speed dial, redial, mute and caller ID2 for both Skype and landline calls. The DPH-50U comes with custom software, two RJ-11 ports and a USB port to connect up the regular phone line, telephone and computer, with the unit drawing power from the computer’s PC port.
The DPH-50U comes with custom software, two RJ-11 ports and a USB port to connect up the regular phone line, telephone and computer, with the unit drawing power from the computer’s PC port. With a fearful eye on Skype’s runaway success, Microsoft has joined the stampede to offer Internet-based telephony services by announcing a cut price, pre-paid PC-to-phone service, the result of a deal with the US telecommunications group, MCI.
With a fearful eye on Skype’s runaway success, Microsoft has joined the stampede to offer Internet-based telephony services by announcing a cut price, pre-paid PC-to-phone service, the result of a deal with the US telecommunications group, MCI. In recent months, Google, Yahoo! and eBay’s Skype unit have all chipped in with their own cheapo PC-to-phone VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services.
In recent months, Google, Yahoo! and eBay’s Skype unit have all chipped in with their own cheapo PC-to-phone VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) services. Similarly, Skype, the current big boys of the PC-to-PC VoIP market, are offering calls for about 2 cents a minute from a PC to a phone in the US other countries.
Similarly, Skype, the current big boys of the PC-to-PC VoIP market, are offering calls for about 2 cents a minute from a PC to a phone in the US other countries. Eniro, the Swedish equivalent of Yellow pages and the phone directory have integrated the Skype URL, callto:, in to their online directories.
Eniro, the Swedish equivalent of Yellow pages and the phone directory have integrated the Skype URL, callto:, in to their online directories. We also understand that they’ll be printing the Skype ID’s in the printed directories for a small fee.
We also understand that they’ll be printing the Skype ID’s in the printed directories for a small fee. Skype has today announced a new version of their Windows release of Skype.For the first time, several more functions are added to make Skype both a more serious communication tool, and at the same time, more frivolous.First the serious side. v1.4, which has been in beta since August, includes call forwarding for when you aren’t sitting by your computer, or if you’re a little more advanced, you’ve dropped out of WiFi range on your handheld version. If Skype finds you unreachable, you can set it to forward your calls to up to three landlines, or mobiles. The forwarding for the person initiating the call is free, with the Skype user paying for the privilege from their SkypeOut minutes.We see the Real Excitement is around the ability to forward calls from one Skype ID to another, giving the ability to have more than one Skype ID. Until now this had to be handled by all sorts of complexity of running two versions, separate from each other. Calls forwarded to another Skype ID are free.What the significance of the whole of Call Forwarding? Your SkypeIn number, or Skype ID becomes your first point of contact, something we’ve seen before with Unified Messaging (UM). UM didn’t set the world alight when it came to techy attention 2-3 years ago, but Skype has timed this perfectly, realising that people are now ready.
Skype has today announced a new version of their Windows release of Skype.For the first time, several more functions are added to make Skype both a more serious communication tool, and at the same time, more frivolous.First the serious side. v1.4, which has been in beta since August, includes call forwarding for when you aren’t sitting by your computer, or if you’re a little more advanced, you’ve dropped out of WiFi range on your handheld version. If Skype finds you unreachable, you can set it to forward your calls to up to three landlines, or mobiles. The forwarding for the person initiating the call is free, with the Skype user paying for the privilege from their SkypeOut minutes.We see the Real Excitement is around the ability to forward calls from one Skype ID to another, giving the ability to have more than one Skype ID. Until now this had to be handled by all sorts of complexity of running two versions, separate from each other. Calls forwarded to another Skype ID are free.What the significance of the whole of Call Forwarding? Your SkypeIn number, or Skype ID becomes your first point of contact, something we’ve seen before with Unified Messaging (UM). UM didn’t set the world alight when it came to techy attention 2-3 years ago, but Skype has timed this perfectly, realising that people are now ready. Personalisation
Personalisation To the sound of a thousand wailing Palm Pilots, Palm has unveiled a version of the classic Treo smartphone running on Windows Mobile 5.0.
To the sound of a thousand wailing Palm Pilots, Palm has unveiled a version of the classic Treo smartphone running on Windows Mobile 5.0. Palm users still waiting for the Wi-Fi card categorically promised at the
Palm users still waiting for the Wi-Fi card categorically promised at the  Carmi Levy, Senior Research Analyst at Info-Tech Research Group commented that the new Treo signals a massive shift in the handheld/smartphone market, adding that “when viewed in conjunction with the sale of PalmSource earlier this month, it’s an acceleration in the demise of the Palm OS platform and final confirmation that its once-dominant position in the broader handheld market is gone for good.
Carmi Levy, Senior Research Analyst at Info-Tech Research Group commented that the new Treo signals a massive shift in the handheld/smartphone market, adding that “when viewed in conjunction with the sale of PalmSource earlier this month, it’s an acceleration in the demise of the Palm OS platform and final confirmation that its once-dominant position in the broader handheld market is gone for good. There’s been no release date set for the Windows-based Treo yet, but it is expected to be available “very early” in 2006.
There’s been no release date set for the Windows-based Treo yet, but it is expected to be available “very early” in 2006.