More details of the intriguing BBC interactive media player, iMP, first made public at IBC 2003, were revealed this evening at a AIGA meeting in London. Sara Watkins, Executive Producer, Broadband, BBC New Media gave the audience further details of what iMP will do and importantly, what it will not.
The most significant revelations were concerning the protection of the content. All content will be DRM’d, only available for a limited period time, once downloaded. As expected, it will also only be available to UK broadband users. In a break with the BBC’s long-standing support of Real, Microsoft DRM will be used for the technical trial, but it appears that no final decision has been made.
Sara started by running a video giving an overview of what the BBC hope the iMP will be and where it might go.
As was known previously, the EPG (Electronic Programming Guide) will cover fourteen days; seven looking forward and seven backward. The programs that have been broadcasted will be downloadable to the computer simply by clicking on them. A preview of a piece can be watched before committing to download a complete show.
Although it was not mentioned in this presentation, in previous discussion we have had we understood that upcoming programs could be selected to download, once they have been broadcasted.
People will also be able to recommend programmes it to friends.
The iMP, originally envisaged by BBC man Ben Lavender, will be a PC-only application that will be downloaded from the BBC website.
Further into the future they are looking forward to having the content on other devices, such as portable music players and even further forward, towards mobile phones. This portable content will initially be limited to audio, as the rights to these programmes are nearly all owned solely by the BBC.
Running through the demonstration version of the product, we were shown the player would have four sections
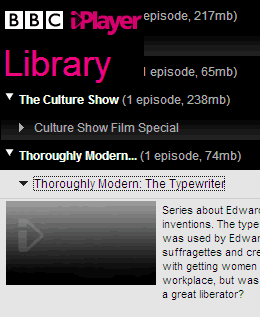
_Library area
A list of the content residing on the computer will be shown, as you would expect from any filing system. A new revelation was that the rights information for each show would be displayed on the right hand side of the screen.
Each separate show will be capable of having its own DRM setting, primarily how many days it will reside on your machine and therefore, how quickly you will need to watch the show before it become unavailable.
The examples given were
Eastenders (most popular UK soap) might be available for two weeks
An episode of Blue Planet (recent super budget natural history programme) might be available for two days.
The amount of compression applied to each piece of content will vary, so the video quality will vary. More popular programmes will be lower quality but programmes that would benefit from better quality will receive it, such as Blue Planet.
_Traffic area
As per standard peer-to-peer (P2P) packages – showing what is being transferred to and from your machine at any time.
It was reiterated that P2P file sharing technologies would be used to automatically exchange content between broadband-connected computers running iMP, thus saving the BBC a considerable amount of money on individually serving each files.
_TV and radio guide areas
No real details were given about this.
Stages of development
The BBC plan to carry out an internal technical trial, where they will work out the logistics of how to get the content from its original source (tape, etc), how to will be encoded, archived and make it available.
Later in the year, possibly around Easter, a closed network of users will be given the product to test it. During this phase they hope to understand how effective the interface design is.
Following these stages they will enter a product development mode – taking all of the learning and re-polishing the product. No date was mentioned for a public release.
During the Q&A session another interesting revelation concerning the Greg Dyke’s idea floated at RTS Edinburgh 2003, the Creative Archive. The content that makes up the Creative Archive will be downloaded using a similar application, but will not be restricted by DRM enabling people to re-edit it, or use it to make other programmes. Importantly it will not be the complete BBC archive, the examples given was – it will be nature programmes but it will not be show such as Dad’s Army (An old very popular comedy show first show in the 1970’s).
AIGA London
Transcript
 The Open Source Consortium (OSC), the organisation leading the charge to make the BBC iPlayer open to all platforms, not just Microsoft Windows, met with the BBC Trust yesterday to find that there was a lot of agreement in their ambitions.
The Open Source Consortium (OSC), the organisation leading the charge to make the BBC iPlayer open to all platforms, not just Microsoft Windows, met with the BBC Trust yesterday to find that there was a lot of agreement in their ambitions. Ben Lavender, the person who came up with the idea behind the BBC
Ben Lavender, the person who came up with the idea behind the BBC  Finally the BBC Trust appears to be open to talking about the iPlayer going Open Source.
Finally the BBC Trust appears to be open to talking about the iPlayer going Open Source. Virgin Media tell us that they “will be the first” TV service to offer the BBC iPlayer service through their STB and remote control – rather than through a computer.
Virgin Media tell us that they “will be the first” TV service to offer the BBC iPlayer service through their STB and remote control – rather than through a computer. The BBC Trust has given the go ahead for the BBC’s iPlayer service (iMP).
The BBC Trust has given the go ahead for the BBC’s iPlayer service (iMP). The BBC has decided to extend the trial for the iMP Player until 28th February 2006, telling trialists that the extra time will enable it to “understand what you want from the service and how you are using it”. A new upgrade of the software is due to be rolled out to the participating trialists in January.
The BBC has decided to extend the trial for the iMP Player until 28th February 2006, telling trialists that the extra time will enable it to “understand what you want from the service and how you are using it”. A new upgrade of the software is due to be rolled out to the participating trialists in January. The BBC’s reaction to such sniping is consistent, if not a little bland
The BBC’s reaction to such sniping is consistent, if not a little bland Despite so much current talk from the UK Telco’s and Sky on the magic that will provide an on demand broadcast TV proposition in the UK, tangible evidence of a working model beyond KiT in Hull and Homechoice is pretty sparse.
Despite so much current talk from the UK Telco’s and Sky on the magic that will provide an on demand broadcast TV proposition in the UK, tangible evidence of a working model beyond KiT in Hull and Homechoice is pretty sparse.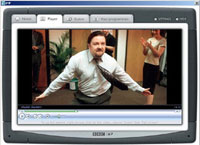 Despite the somewhat limited selection of programmes, which I’m told is largely down to copyright issues, it seems a positive move for a public sector broadcaster actually providing a service and solving the ‘problem’ of letting you see a programme you forgot to record or you later discover is worth viewing.
Despite the somewhat limited selection of programmes, which I’m told is largely down to copyright issues, it seems a positive move for a public sector broadcaster actually providing a service and solving the ‘problem’ of letting you see a programme you forgot to record or you later discover is worth viewing.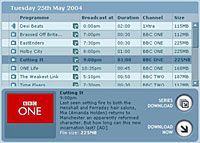 The BBC is thinking beyond the present Windows-only solution. Speaking recently in London the BBC’s Project Director for iMP Ben Lavender reinforced the BBC philosophy of platform agnosticism and spoke of the desire to work on Apple and Linux solutions when DRM issues can be satisfactorily dealt with.
The BBC is thinking beyond the present Windows-only solution. Speaking recently in London the BBC’s Project Director for iMP Ben Lavender reinforced the BBC philosophy of platform agnosticism and spoke of the desire to work on Apple and Linux solutions when DRM issues can be satisfactorily dealt with.