There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
Ofcom has a duty to ensure spectrum isn’t wasted and as a consequence of the auction will end up driving revenue for the Government. Previously, and famously they did very well when they auctioned the 3G licenses, raising £21bn for the Treasury.
They recently auctioned some GSM spectrum and that only raised £3.8m, but it was much less than the 3G lot with many more restrictions.
Under its new face, and following EU directives, Ofcom likes to offer technology neutral licenses, which means the licensee can use the spectrum for whatever they want – as long as they meet the radio restrictions on that band (power, spectral masks, etc). They hope this will stimulate innovative services which is good for the economy.
There’s a lot of interest in the spectrum, as it could be used for lots of services including 3G and WiMAX, but that’s where the problems start.
Possible European Interference
There are various blocks of spectrum which are coordinated at a European level and each EU country uses the spectrum for the same things. That’s pretty much what happens for GSM and 3G, as well as some TV and radio bands.
It’s all organised by CEPT (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications) and the Radio Spectrum Committee (RSC), CEPT is represented by 47 countries and the RSC by 25 EU states. They ensure that radio usage is coordinated. Unfortunately radio waves don’t abide by national borders, so it would be no good if one country was using spectrum for say TV and another for radio as they’d interfere with each other.

Though the UK is an island, interference issues are quite common, especially in the south east with France and the north east with the Dutch and even the Nordic countries. The west has to worry about Ireland (and of course Northern Ireland abides by UK policy).
These particular bands are already allocated for 3G, 10MHz in 2010 – 2020 MHz, is already designed for license-exempt self-provided, self-coordinated IMT-2000 use. In the UK none of the 3G networks have actually utilised it, though in other parts of Europe it has been used for this purpose.
2500 – 2690 MHz is currently mainly used for video broadcast systems, all licensees have been given notice to vacate by 31st December 2006. This is a significant amount of spectrum (190MHz) which is greater than is currently allocated to the whole of 3G use (140MHz). It was reserved for a “new” entrant if the current 5th 3G operator failed or for existing 3G expansion.
Ofcom’s suggestions summarised
Ofcom are currently holding UK consultations to see what stakeholders think should happen. They are proposing the following: –
2500-2690 MHz Packaged on the basis of blocks of 5 MHz as lots of paired spectrum (2×5 MHz, 120 MHz duplex spacing) and unpaired spectrum (5 MHz), with the eventual amount of lots in each category to be determined in the auction. The reference point is as per the CEPT band plan: 14 lots of paired channels (14x2x5 MHz with uplink in 2500-2570 MHz and downlink in 2620-2690 MHz) and 9 lots of unpaired channels (9×5 MHz in 2570-2615 MHz).
One guard channel will be necessary at adjacencies between paired and unpaired spectrum, at 2615-2620 MHz, and possibly another in the top part of the band.
There is a possibility to allow paired lots to be converted into the equivalent of two unpaired lots in the event that demand for unpaired lots exceeds that for paired lots at a given lot price.
Each bidder should receive contiguous lots in each category, except potentially one assignment of unpaired spectrum which could need to be split into two blocks of contiguous lots.
2010-2025 MHz Package for award as a single 15 MHz lot.
2290-2302 MHz Package for award as a single 10 MHz lot and retain 2300-2302 MHz for possible inclusion as part of a future award together with 2302-2310 MHz.
What might the response be?
The consultation will close in March 2007 and it’s likely the 3G operators will be extremely vocal in their claim to this spectrum, as they paid so much for their original licenses.
Once Ofcom digest the responses, they’ll then have to argue the case at the European level to ensure it can be licensed off in a technology neutral manner without upsetting our neighbours, however getting agreement from at least 47 countries tends to be a time consuming process.
Luckily CEPT are already discussing the issues and are expecting to make a statement in July next year. RSC will follow shortly after.
Although there’s no guarantee that discussions will go in Ofcom’s favour, they are hoping an award process can start in the Autumn of 2007, though it may well be delayed until 2008.
Potential Cash
With 16 national licenses available, there’s a fair amount of cash the government can expect to raise. Even if Ofcom set the minimum price at £50,000 then that’s £800,000 – they are likely to reach much higher values, although not the silly pricing that the original 3G licenses fetched.
Ofcom
CEPT (European Conference of Postal and Telecommunications)
Radio Spectrum Committee (RSC)
 Samsung has launched what it claims is the first mobile phone in the known universe to come with an optical joystick.
Samsung has launched what it claims is the first mobile phone in the known universe to come with an optical joystick. The slide-open phone also comes with an illumination sensor which automatically controls the brightness of the LCD screen and keypad, so you won’t be dazzled if the phone goes off in the middle of the night.
The slide-open phone also comes with an illumination sensor which automatically controls the brightness of the LCD screen and keypad, so you won’t be dazzled if the phone goes off in the middle of the night. The rumours of Niklas Zennstrom of Sweden and Janus Friis of Denmark next project have been whirling around for about six months since
The rumours of Niklas Zennstrom of Sweden and Janus Friis of Denmark next project have been whirling around for about six months since 
 While announcing the release 3.0 of their VoIP software, Skype have unveiled the US Unlimited Calling Plan.
While announcing the release 3.0 of their VoIP software, Skype have unveiled the US Unlimited Calling Plan. Those Europeans who are surprised that calls to mobiles are included, should know that in the US owners of mobile pay to receive calls, so callers don’t pay extra to make them.
Those Europeans who are surprised that calls to mobiles are included, should know that in the US owners of mobile pay to receive calls, so callers don’t pay extra to make them. There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
There’s a fair chunk of spectrum that’s sitting there not being used in the 2GHz band. The various bits are 2500-2690 MHz, 2010-2025 MHz and 2290-2300 MHz.
 O2 Ireland has become the first European mobile operator to offer Napster Mobile.
O2 Ireland has become the first European mobile operator to offer Napster Mobile. O2 has spend a considerable amount of money tying themselves to music, attempting to benefit from all of the ‘cool’ that it can bring. You only have to witness the party they threw at IFA last year to understand how successfully they’ve been with it – it was definitely the best party at IFA, rammed full of young things gyrating.
O2 has spend a considerable amount of money tying themselves to music, attempting to benefit from all of the ‘cool’ that it can bring. You only have to witness the party they threw at IFA last year to understand how successfully they’ve been with it – it was definitely the best party at IFA, rammed full of young things gyrating. Waterproof gadgets aren’t just for the lounging by the pool in the summer. Despite its rather alarming name (“Stop the ferry! iPod overboard!”), this case promises to protect your tunes from the worst the winter weather can throw at you, as well as providing full waterproofing to a depth of six metres for summertime use.
Waterproof gadgets aren’t just for the lounging by the pool in the summer. Despite its rather alarming name (“Stop the ferry! iPod overboard!”), this case promises to protect your tunes from the worst the winter weather can throw at you, as well as providing full waterproofing to a depth of six metres for summertime use. The case comes with a small eyelet for a lanyard (supplied) and a large Velcro armband. This is tougher and more comfortable than the standard Apple armband, for example, and closes very firmly – a quality piece of kit. Assuming you want to read your iPod’s display and have the headphone jack upward, that means the seal faces downward – another potential concern if the seal were to accidentally open while you’re running.
The case comes with a small eyelet for a lanyard (supplied) and a large Velcro armband. This is tougher and more comfortable than the standard Apple armband, for example, and closes very firmly – a quality piece of kit. Assuming you want to read your iPod’s display and have the headphone jack upward, that means the seal faces downward – another potential concern if the seal were to accidentally open while you’re running. Channel 4 are having problems delivering their 4OD, Geo-restricted content to their UK-based consumers.
Channel 4 are having problems delivering their 4OD, Geo-restricted content to their UK-based consumers.
 Marty Lafferty, CEO of the Distributed Computing Industry Association (DCIA) concludes his synopsis of the Next Generation P2P sessions at the recent
Marty Lafferty, CEO of the Distributed Computing Industry Association (DCIA) concludes his synopsis of the Next Generation P2P sessions at the recent 
 Marty Lafferty, CEO of the Distributed Computing Industry Association (DCIA) gives us a synopsis of the Next Generation P2P sessions at the recent
Marty Lafferty, CEO of the Distributed Computing Industry Association (DCIA) gives us a synopsis of the Next Generation P2P sessions at the recent  Daniel Harris (pictured right) provided Kendra’s perspective on P2P from its alliance of content owners and software makers. Daniel’s vision is that any application on any device should be able to browse any catalog, and there should be universal interoperability. Record labels have had different ways of managing their catalogs, historically; now we need to show them that with P2P it is possible to aggregate databases and achieve across-the-board content monetization. P2P can bring benefits of non-centralized search and publishing to all sorts of content databases.
Daniel Harris (pictured right) provided Kendra’s perspective on P2P from its alliance of content owners and software makers. Daniel’s vision is that any application on any device should be able to browse any catalog, and there should be universal interoperability. Record labels have had different ways of managing their catalogs, historically; now we need to show them that with P2P it is possible to aggregate databases and achieve across-the-board content monetization. P2P can bring benefits of non-centralized search and publishing to all sorts of content databases. More than 1 in 3 European households will have an integrated home network by 2010, according to a new industry report from Understanding & Solutions.
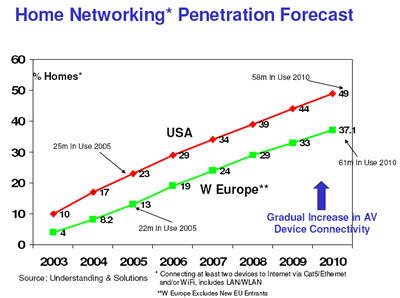
More than 1 in 3 European households will have an integrated home network by 2010, according to a new industry report from Understanding & Solutions.