 We had a chance to sit down with Dan Marks, the CEO of BT Vision, at the point where they were going through finalising what would make up the BT Vision offering.
We had a chance to sit down with Dan Marks, the CEO of BT Vision, at the point where they were going through finalising what would make up the BT Vision offering.
Listen to the audio interview
They had just shown the service for the first time to a select number of journalists.
The discussions covered the development and importance of the EPG; why he thought that BT Vision would be different from other offerings (lack of subscription being a large part of it); the type of content they planned to be offering on it.
We also find out his thoughts on developing with Microsoft; why User-generated content is an important part of the BT Vision service; his views of the 7-day ‘watch-again’ feature (that we think they’ll be launching without) and towards the end, how content producers would work with BT, to sell their content through BT Vision.
It will be interesting to see how much of this has changed between the interview and the launch later today that we’re covering live.
Digital Lifestyles: Simon Perry of Digital Lifestyles here with BT on their Total Lifestyles Day. Just been looking at BT Vision IPTV service. I’m with…
DM: Dan Marks, Chief Executive BT Vision. Nice to be here.
DL: Yes, it’s an impressive demo. Lots of good features there. Not only does the box look smart but also I was impressed by the look of the interface as well. It’s got that thing where you click on the function it zooms towards, it gives a feeling of being connected with the box rather than a lot of the dead feeling you get with other boxes as well.
DM: Yeah, I think that there are a number of things that you need to do well to make IPTV work for customers and work commercially, and one of them is clearly you have the content people want, and you have to make it available to them when they want it and how they want it. And secondly, you need to make it available to them on the terms they want it. This is something that’s stopped development in the pay television sector past 15% of UK TV households. A high price, long term subscription commitment is very off putting to at least 50% of the UK who don’t want it, so that’s the second part of what we do that was attractive, I think. And the third thing that I think we do very well is to have a fantastic EPG, and by fantastic I mean some of the things that you recognized. It has to be simple, it has to be intuitive, it has to be fast, and it has to both help you in navigation and in promotion. If you can do that I think you got a possibility that you could have a winner, and of course I’m biased but I think we held those.
DL: I mean that’s interesting, three things you count there, if we pick up the EPG as the last one, one of the things I find with previous services though, is when you’ve got a wide selection of content and you sit down to watch a film, maybe it’s just me but I find that it almost slightly overpowering about the amount of choices that I had, and you sit down there and you sit down watch the trailers. Because you want to spend the limited amount of time you have in your spare time, you want to spend that doing, seeing the best film that you can at that very moment. Have you got a way of recommendations of videos, or you’ve seen this one before you’re going to like this one as well, so people don’t have to go through the alphabetic list as well as some other ones, and there’s editor’s choices which is a good idea. Is there any other way of accessing the content?
DM: Well, I think that you’re right to pull out a couple of ways that we can editorialize the EPG to help people find the content that they want, but increasingly as we develop the sophistication of the platform, and develop intelligence into the system, we’ll be able to help you to find what you want by knowing something about your choices, what you like. I think recommendations are certainly part of the roadmap. I think the ability to show Picture in Picture from the EPG is terribly important. I think that the opacity of the EPG is very important, so that you don’t lose the fundamental viewing experience.
DL: So you don’t feel disconnected.
DM: You don’t feel disconnected and move quickly from one thing to the other. I think we will feel successful if our customers don’t know and don’t care where they are, meaning don’t know and don’t care whether they’re watching broadcast, television, our on-demand asset, or they’re in some other kind of interactive area. It doesn’t matter to customers. They shouldn’t know or don’t care if something is played off the hard drive or out of the network. What people want is very straightforward. They want what they want, they want it when they want it, they want it on the terms of they want, and they want to be able to get it. And that’s the key point, all the rest is transparent.
DL: I thought the idea of including the free view tuner in there, very smart idea, because therefore you don’t need to pump that content over the network as well. You’ve got stuff coming from free over the air.
DM: That’s right. There’s two ways to look at it. The way that we looked at it is that it’s serving a customer need. One can look at it in terms of competitive differentiation or technically, I’m happy to address those things. But fundamentally the reason that we’re doing it is because it addresses a consumer need. People want free view and they don’t want to pay additional charge because it gives them more or less what they want. So why not give them that.
DL: They’re comfortable with it and you can see they’re buying them in large numbers and all.
DM: That’s right. So why not give them that and build on that? And from a differentiation point of view, this is the key point. Our service doesn’t have a mandatory subscription, just like free view. Sky and Cable do. Mandatory high price, long term subscription commitment is exactly what 50% of the UK do not want, there’s not much point in trying to give that to them.
DL: But what do you think is restricting them? You must’ve done research on that. What’s restricting them on not going for the subscription services?
DM: I think a variety of things that, it’s not that they don’t want more television, more choice, more convenience, more control, they just don’t want it on those terms. They don’t buy the proposition that more volume equals more choice. I don’t buy that proposition in my life. I don’t think you do. When you go to Sanspree’s you don’t have to buy eggs and cheese if you want to buy some milk. We live in competitive marketplaces. You don’t have bundling. Or if there’s bundling, there’s bundling to serve the consumer rather than to force the consumer into payment commitments that are slightly more than what they’re comfortable running. This is a legacy of technology and history. We are coming into this marketplace to offer people the alternative to that, and I think that there’s a huge consumer demand for it.
DL: And with the content deals, you said one of the key parts is content.
DM: Yes.
DL: What sort of content have you got together and what are you hoping to get before you launch the servers?
DM: Well, we’ve announced about a dozen content deals with major content owners from studios to music majors, to the BBC, some of which are really quite innovative. Our deal with Endemol and with Warner Music and with Turner, all includes an element of exclusive content that we’re going to be making specifically for our platform.
DL: For a period of time exclusive, for a period of time, or fully exclusive?
DM: Well, we’ll see what we’ll do with it but eventually it’s fully exclusive. It’s a way of developing content which is placed to extract the interactive abilities of the platform, and I think I’m not trying to tell you that we’re going into the production business and making conventional linear television programming. We’re not. We don’t have any aspirations in that area.
DL: That’s definitely is it that you’re not going to get into the production side?
DM: Well, for the immediate future, we’re not, no. We’re in the acquisition business. We think that we can develop interactive content very successfully.
DL: So are you taking shot content and making interactive parts from that really, right on the BT television platform?
DM: Well, there are so many opportunities. What the interactive back channel and this service can do is almost unlimited. Move from television programs and into games. You can move from games to on-demand content. You can move from one on-demand content to participation opportunities. You can move from there into advertising and sponsorship opportunities. You can move from those to retail opportunities. You can move back from there to broadcast or from broadcast and into retail.
DL: So you’re saying it’s more or less on-demand? [laughs]
DM: It’s more or less on-demand. So you can make red button interactivity into a very powerful opportunity for consumers.
DL: So do you think that’s something that BT Vision, or part of BT Vision will be doing, is creating the interactivity part then? Or will you be having the production part doing that for you?
DM: I think we’ll work with partners. But it’s difficult to separate who does what in these things. We have people who work in my team who are interactive programmers, specialists, interactive marketing specialists. The guy who run that business is called Anthony Carbonari, and he joined us from Disney where he ran Disney’s broadband business. Before that their mobile business, and before that FT.com’s global ad sales business. So we have people in the team who are really deeply experienced at interactive television, and we are able to work with partners of all sorts, whether they’re broadcast partners or content owners or interactive applications manufacturers/developers, hardware developers. We can work with them to bring their product to a maximum number of people possible.
DL: Can you give me an example of these innovative deals with Endemol Warner that you mention? Can you give me an example of the innovative part of those, apart from exclusivity?
DM: Apart from the exclusivity, we haven’t announced exactly what the products are that we’re developing.
DL: Don’t feel like you need to hold back. [laughs]
DM: I do appreciate the opportunity. I understand it’s just between you and me and all your listeners and readers, but forgive me on passing on that.
DL: Okay. Is that coming soon though?
DM: Yes.
DL: I mean just innovation is what people obviously get excited about, so it’s good to hear about that.
DM: I mean there are a few other content highlights that I think is worth mentioning. We did conclude a deal recently with the FABL for premiership football.
DL: Now what was the wording on that? It was near-live wasn’t it?
DM: Yes.
DL: What’s the delay for near-live?
DM: The games will be available after ten o’clock on match day.
DL: Ten PM? Okay.
DM: And they’ll be available for 50 hours, on-demand, and we will make 240 tournament games per season available which represents two-thirds of the games played. So on average, two thirds of your clubs games will be available from us for 50 hours at ten o-clock on match day. It’s pretty good. And the best games of the previous month will be available for the next month.
DL: Is that done through voting of people saying that “this is the best game”, or is that done on editorial choice on your part?
DM: That’s an editorial choice on the part of some particularly expert people. We will be making those games available to people either on a subscription basis, club subscription, total football subscription, or on an individual pay-per-view basis. And we think we’ll be the only place where you can get pay-per-view on-demand football.
DL: Interesting.
DM: I think that’s a real demand for that, people may not want to have a very high priced subscription to a linear service for live football which anyway they don’t always see. And I think that next to that, well there are a lot of people who do want, if that’s what people want then they’ll definitely subscribe to Sky pay. But those people who want something more flexible, I think we can provide them with just the sort of service that they desire.
DL: Yeah, I guess if they hear that a game is particularly good, say maybe on the news they’ve see highlights from it, then they can decide to pay-per-view it ten o’clock that evening, even if it’s not their own team.
DM: Exactly.
DL: Well, that’s the content side. The rollout of it, having seen the demo I was really surprised to hear that it’s going to be running on a two-meg service. That’s really encouraging, and to be applauded on your part to have TV-quality, to be able put out a two-meg service.
DM: I think that it looks pretty good for two-meg, and it’s going to get better as we compress, we use mpeg4. And I think it’s going to get better and better. It’s really only at the beginning of the journey that each compression technology makes, and it’s a journey of increasing efficiency.
DL: And is quality of service on the line? First of all, do you have to be a BT broadband subscriber to use the service?
DM: Yes.
DL: I saw the new hub today. Great looking piece of white plastic. Something people will be proud to put on their lounge as well, rather than stick it under the stairs.
DM: That’s nice of you to say. I agree with you.
DL: And there’s a quality of service for BT Vision, is there?
DM: There’s a quality of service for BT Vision.
DL: So that would override other PCs accessing the network in the home?
DM: Yeah. We guarantee the two-meg bandwidth end-to-end and ping bandwidth, so that we can guarantee to deliver glossy pictures, speed, you don’t want to wait.
DL: There’s lots of exchanges being changed to eight-meg as well. What sort of percentage of those are done so far, do you know?
DM: I know that we’re serving 93% of the population of two-meg now, and there was a, as you know year, 8-year or 18-month changeover to the up to eight-meg proposition. And that additional bandwidth and the increasing efficiency of compression has been able to allow us to either serve multiple boxes in the home or perhaps use it to stream HD, let’s see how that compression, how much bandwidth it takes to do that I don’t know.
DL: But I mean my stuff has been showing HD over hardly anything that I see at IDC.
DM: Really? Only to a PC?
DL: No, it was to their IPTV box.
DM: Well that’s pretty impressive.
DL: I think I might be one-meg. It sounds ridiculously low but I think I…
DM: Yes that sounds very low but I’m delighted if… We are, as you know, in business with Microsoft. They’re providing the platform.
DL: So that’s their IPTV box is it?
DM: It’s a Phillips box. Microsoft has a media center, which is their sort of PC, it has a media box, it’s a pretty smart box. This box is made by Phillips. Microsoft IPTV is the software, is the middleware.
DL: Okay. Have you been satisfied by Microsoft IPTV so far?
DM: We’re very confident that we’re going to launch in New York, that it’s the reason that we want Microsoft is because we think that it’s likely that Microsoft is the industry standard. From air to air, there’s a huge advantage to be associated with the middleware that is the industry standard.
DL: I know that they’re very keen if not totally obsessed with it working, the IPTV stuff. I’m just reflecting back on other cases where they’ve had IPTV installations around the world and had some difficulty with it. You haven’t had any road bumps with that?
DM: I think it’s pretty clear that it’s not easy to do this. Technically it’s not an easy thing to do. There are at least three layers of complexity to getting an IPTV service such as the one that we’re running out. The first is the middleware, and as everybody knows it’s been in development and it’s not concluded, but Microsoft are a very big company, a very capable company, and as you said very focused on getting it right. So we’re confident that that would happen. However, it’s not there, and we’re not entirely in control of that process. And the sort of box that we have, the sort of service that we have, which is a hybrid DTT-DSL service, is unusual. The second level of complexity is the box, and the third level of complexity is the network.
DL: Well, thank goodness you control one of those [laughs]
DM: Which one of those?
DL: The network.
DM: Well, I don’t control that network.
DL: Right, but within the same organization.
DM: Yeah, but it’s on the other side of a very high very broad Chinese wall, I simply don’t control the timing, customers, BT wholesale, in the same way that anybody would be accustomed to BT wholesale. The complexity is that each one of those tasks, building a new middleware solution or platform, especially that works that’s a DDT-DSL hybrid, building a complicated and really advanced set top box, the PVR, dual DDT tuners, DSL connection, HD-ready, CA-ready, this is also complicated. And the network, the interaction between the three of them is complicated. So I’m not in control of any of those elements. I am an active customer of the company, active in a sense that I’m highly motivated to get it done and quite competent in some of those areas, as a business. But it’s complicated. So as we sit here today, no showstoppers to launching in the autumn.
DL: Okay. Well obviously it’s too late now to change platform anyway even if you would want to. One of the things that I heard about recently is Sky’s plans for their next generation box.
DM: Fantastic. Tell me everything.
DL: Okay, I’m sure you know most of it already. They’re incredibly ambitious with the number of channels it’s going to receive. Standard would be four channels, but up to twelve seems like an extraordinary.
DM: Four to twelve channels of what?
DL: Of satellite into a home. So the ability to receive up to 12 LNBs on that.
DM: What does that translate into, in terms of a customer’s experience?
DL: Well, of course, the first question would be why would people need that much?
DM: Well what does it actually give you? What does that mean for the customer?
DL: The reason to have four, which is the base level, which is pretty high, record one watch one. And one for pre-delivered content to go to the hard drive. The other one probably for another box around the house, a thin client somewhere in the house. And that’ll be the same for the other 12 channels as well.
DM: Is this a box with an ethernet port?
DL: No, that’s without the broadband connections. That’s straight from satellite, which is an extraordinary, especially if a lot of those are HD as well, extraordinarily ambitious.
DM: I wish them the very best of luck.
DL: [laughs] Do you think that’s much of a threat to you, the fact of them coming out with a next generation box and then running a network around the house and the ability to stream content?
DM: Look I think that Sky are an extraordinarily competent organization.
DL: Frighteningly so, sometimes.
DM: No, I’m not frightened of them. I just said that they’re an extremely competent organization in many ways. The truth is that we’re all moving into the same territory but we’re moving there from different positions. We all have different strengths. While Sky is competent in something, BT is fantastically competent at others. Sky has eight million television customers, and BT has nineteen million non-television customers. We have a fantastic brand, which is deeply trusted by the UK public. We have strength and depth of marketing resource of customer support, of engineering knowledge, of network management knowledge, and these are fantastically valuable advantages. They, are collectively, I just mentioned a few of them, it would make a very long list of the things that BT has…
DL: I’m glad you didn’t, thanks for that [laughs]
DM: [laughs] But these are the reasons I am here because I think that with those advantages and with the strategic imperative of the changes of broadband let’s say, that has brought a strategic imperative of getting into high value services, of doing the sort of thing you see today, I think BT has a very, very strong chance of emerging from this process as the leading broadband company. And that means telco broadband, including entertainment. I mean I think it’s a combination of things. It has a strategic, it has a high motivation because the conventional calls and lines business is clearly not a growth business, to say the least. It has a very competent management and a very clear direction, we have made a very significant commitment to this kind of business.
DL: One of the things you mentioned as well was the possibility of having other boxes around the home once you get more bandwidth available to you.
DM: Yes.
Would you have a central box or would you have a number of BT Vision boxes around the house, or would you have a central server and sort of a thin client?
DM: Not yet decided what the relationship between the hub and the boxes and technically how the connections between the hub and box.
DL: Yeah. Okay. And how insistent have the studios been on content protection?
DM: I think every responsible owner of content, not just the studios, is very concerned about piracy and the threat to their livelihood. And I think the fact that we are able to provide such strong protection to their program is very important. At the heart of our business is to make strong partnerships with those people.
DL: And would you be able to take the content down from the BT Vision box down to portable devices?
DM: Not from launch. The box isn’t designed to do that but there’s no reason why we shouldn’t make the content available to the PC, rights permitting.
DL: Passing them on to more portable video players.
DM: Generally speaking, those sorts of things are connected to PCs in most people’s homes. They’re not entirely giving them away. There’s no reason why we shouldn’t deal to make programming available to people to those devices, given the rights. There is some, still some concerns about that from a rights perspective.
DL: If it’s running a Microsoft DRM on all platforms they would feel more relaxed if not fully relaxed about that.
DM: They would feel more relaxed. It’s a process to get everybody comfortable.
DL: Okay. You were talking about that you hoped to have TV replay, the ability to have the last ten days worth of content available, that those discussions ongoing with the BBC and any other…
DM: Well it’s largely dependent on rights, and how those things come out. BBC have indicated that they want to make the last seven days BBC programming available as a type of public service repeat. On principle it’s something that we support. There are quite complicated rights negotiations involved in getting to that part.
DL: It seems that some of their programming, ones that they’re in control of where they haven’t got a third party production company involved, it becomes a lot easier for them to be able to say, right, seven days of that content will be viewable. You just look at it again.
DM: Well yeah, they’ve more or less agreed the seven-day principle. I think they have agreed the seven-day principle with PACD, which is the Producers for Independence. So it seems very likely that a seven-day public service window for BBC programming will emerge. I’m not sure if that’s going to be the model for all broadcasters. I think it’s definitely a different situation when programming has been funded from public purse, than the situation when the program has been funded from advertisement or other commercial sources.
DL: One of the things that I wanted to chat to you about, that it was pleasing to hear, that there was going to be support for user-generated content as well. Because I wondered how open the platform is going to be for other people to put their content onto it, small production companies or even individuals to do that.
DM: Well, we are going to be making some specific announcements about niche content and user-generated content over the next few weeks and months. But in general we think that the interactivity about which we spoke earlier and niche content, user-generated content, are fantastically important for the viability of our business. We think that it’s what we can do uniquely well, both in terms of the technical capabilities of the platform, and as a result of BT’s relationship with its customers and its reach. And our vision is that there is a place on the service for blocks of programming that haven’t found a place in broadcast television because they appeal to smaller interest groups, and those interest groups are going to be very well served by this service. They are any way well motivated to find content. They want to talk to each other. They want to interact with that programming and with each other. And therefore this is a model platform. So we intend on making programming available on-demand. We intend to enable video telephony, IM, retail, games, and other communicational opportunities around that programming, and make really satisfying areas for interest groups to visit. And these interest groups range from very, very small, to pretty big, but none of them are particularly well-served on broadcast television.
DL: Well, because it’s a mass medium. You’ve got the quantum shift.
DM: It’s one way. User-generated content we also think is tremendously important. What we’re doing is converging functionality from telephones, PCs, into the living room in so far it makes commercial sense, in so far as it makes sense to our consumers, where there’s consumer demand. There’s no point in doing everything that you’re able to do on a PC, or on a mobile, or on a PDA, in the living room, because some of it just doesn’t make sense. Some of it is a lean forward experience, a one-foot experience. This doesn’t work in the living room, but some of it does.
DL: So you’ll have a keyboard add-on for the…
DM: Not at launch, but that’s very likely. The stuff that happens in the living room is probably not really keyboard-oriented.
DL: I always have a laptop on, close to hand, and in the rare experiences where I did watch TV.
DM: I might venture to guess that you’re an unusual sort of television viewer [laughs].
DL: Well, I think that the actions of people these days who’ve been involved in this area for a long time, quite possibly foretelling what the masses will do anyway. It depends on whether you’re a passive viewer of television or whether you’re an active viewer of television.
DM: Indeed it does.
DL: Perhaps if somebody wants to find out more detail about it and the program isn’t giving you the detail, or the interactivity around the program isn’t giving you the detail you want to receive, then and I think you need another form to sort of..
DM: Yes, and there are lots of ways that that searchability, which is really what we’re talking about. How you find stuff in a sophisticated way, might take, might go towards voice activation. I’ve actually seen some voice activation using the handset…
DL: You’re saying that it’s finally..
DM: You say what it is that you want. It finds it from a huge, huge, huge library. So it might very well go that direction. There’s an awful lot you could do with intelligent design of the UI and cursor movements triples out. There’s an awful lot you could do as you build in terms of a simpler system. I’m not sure all of it requires a keyboard, but we’ll see how that develops.
DL: If we just wrap up on the content side, you’re saying you’re interested in small producers and user-generated content. How would somebody go about, if there’s an incredibly vibrant small production company, how would they get their content onto BT Vision?
DM: First of all they have to have the rights.
DL: Well if they’re producing it, it’s their idea, they’ve shot it, it’s amazing.
DM: I should say that it’s unlikely that we’re going to be in the production business, so we’re probably not going to be co-producing or coming in early in the production cycle. But if production companies or owners of rights have rights to programming or to interactive content that they want, that they feel is right for this service, then they should contact us.
DL: And there’s a contact, a production person they should speak to.
DM: Well we have a department of acquisitions people. Or they can always write to me and I’ll pass it to the right place.
DL: Okay. Of the deal, say that the small production company, what sort of percentage split would be worked out on the, let’s not think about how much they might charge for it, but what’s your model for the income split?
DM: I think that it would be inappropriate for me to divulge the details of other people’s commercial relationships.
DL: I’m not interested in theirs, I’m interested in what it would be for a small production company.
DM: Yeah, I think that that would be something that we would discuss with somebody on a case per case basis.
DL: Yeah, there’s no range that you’re happy to talk about?
DM: No.
DL: Okay. And user-generated content, that’s mostly people that are doing it for fun and for free. Is that something that’ll be fun and free for BT Vision people to watch as well?
DM: That all depends on, we often don’t have cost for rights but we usually have costs for distribution. So that all depends on what the advertising model is, the sponsorship model, where’s the money coming from. It could be subscription, it could be advertising, it could be sponsorship. But not charging for rights doesn’t mean that it’s free all the way down the line. That maybe a very good reason to making it free to customers and it may not be. We’ll cross that bridge when we come to it.
DL: Okay. It’s been very good, thanks, I know you’re busy today so I appreciate the time.
DM: Not at all, pleasure to meet you.
DL: And well let’s get together and chat over more, because there’s so much to this. I think that there’s a lot to be explored here.
DM: Keep coming back and keep talking to us and see how this thing develops.
DL: Great, thanks for your time.
DM: Thanks a lot.
 As we’ve been covering for ages, Korea is super forward in many things electronic.
As we’ve been covering for ages, Korea is super forward in many things electronic. The Koreans are achieving this by the EXIM standard for online and mobile music service. EXIM stands for Export/Import which was developed Korea’s Electronic & Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and INKA Entworks. It should be wide reaching as up to 90% of online music sites and 70% of portable music devices deployed in Korea at the moment use DRM solutions based on the EXIM standard.
The Koreans are achieving this by the EXIM standard for online and mobile music service. EXIM stands for Export/Import which was developed Korea’s Electronic & Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and INKA Entworks. It should be wide reaching as up to 90% of online music sites and 70% of portable music devices deployed in Korea at the moment use DRM solutions based on the EXIM standard. SK Telecom, the largest mobile provider in Korea as finally agreed to open up their handsets and service to allow music from third party services to be used. Until now only content authorised by SK could be loaded onto their phones.
SK Telecom, the largest mobile provider in Korea as finally agreed to open up their handsets and service to allow music from third party services to be used. Until now only content authorised by SK could be loaded onto their phones. O2 Ireland has become the first European mobile operator to offer Napster Mobile.
O2 Ireland has become the first European mobile operator to offer Napster Mobile. O2 has spend a considerable amount of money tying themselves to music, attempting to benefit from all of the ‘cool’ that it can bring. You only have to witness the party they threw at IFA last year to understand how successfully they’ve been with it – it was definitely the best party at IFA, rammed full of young things gyrating.
O2 has spend a considerable amount of money tying themselves to music, attempting to benefit from all of the ‘cool’ that it can bring. You only have to witness the party they threw at IFA last year to understand how successfully they’ve been with it – it was definitely the best party at IFA, rammed full of young things gyrating. BT are pushing BT Digital Vault, their product to store all of your digital data on, to that end they’ve just launched a Web service to calculate the value of your digital output.
BT are pushing BT Digital Vault, their product to store all of your digital data on, to that end they’ve just launched a Web service to calculate the value of your digital output.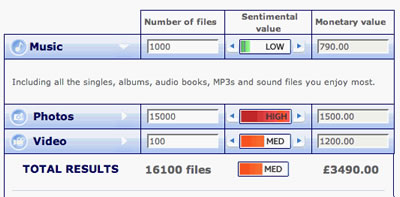
 The BBC has announced it is running a push-VoD trial in the UK.
The BBC has announced it is running a push-VoD trial in the UK. The potential for this is huge – both with general interactivity and specifically with games or educational material.
The potential for this is huge – both with general interactivity and specifically with games or educational material. What are Ajax homepages?
What are Ajax homepages?
 Channel 4 are having problems delivering their 4OD, Geo-restricted content to their UK-based consumers.
Channel 4 are having problems delivering their 4OD, Geo-restricted content to their UK-based consumers.
 MySpace has announced that they will be scanning the user accounts on the service, deleting those of registered sex offenders.
MySpace has announced that they will be scanning the user accounts on the service, deleting those of registered sex offenders. MySpace has had to juggle with the fear of parents that their children are making themselves targets for unwelcome attention from those wishing to do harm to them.
MySpace has had to juggle with the fear of parents that their children are making themselves targets for unwelcome attention from those wishing to do harm to them. There’s always a lot of interest around Halo, the signature game for the Xbox.
There’s always a lot of interest around Halo, the signature game for the Xbox. Two years later and the machine is grinding into action again to let the public know about the non-imminent arrival of Halo 3. It’s expected for release during the third quarter of 2007, and will, of course, run initially exclusively on Xbox 360.
Two years later and the machine is grinding into action again to let the public know about the non-imminent arrival of Halo 3. It’s expected for release during the third quarter of 2007, and will, of course, run initially exclusively on Xbox 360. US television giant ESPN has just announced that it will be purchasing NASN, the only European channel dedicated to North American sports.
US television giant ESPN has just announced that it will be purchasing NASN, the only European channel dedicated to North American sports. We had a chance to sit down with Dan Marks, the CEO of BT Vision, at the point where they were going through finalising what would make up the BT Vision offering.
We had a chance to sit down with Dan Marks, the CEO of BT Vision, at the point where they were going through finalising what would make up the BT Vision offering.