 Broadband is taking off everywhere, speeds are increasing and everybody’s happy. Well almost. Broadband isn’t available to all, especially those in more rural areas.
Broadband is taking off everywhere, speeds are increasing and everybody’s happy. Well almost. Broadband isn’t available to all, especially those in more rural areas.
Unfortunately cable companies don’t have the financial resources to lay fibre everywhere (especially in today’s economic climate) and even BT, who are radically changing the old telephone network so that every exchange in the UK is wired up for Internet, still won’t be able to reach rural customers. It isn’t because they don’t want to, but (in BT’s case) the DSL (digital subscriber line) technology just doesn’t work at long distances.
This will leave large percentages of the population without broadband and currently their only option will be expensive satellite systems.
There’s a chance that some kind of fixed wireless access (FWA) solution will become available, but currently the technology is expensive and again requires a massive investment in radio masts and connecting them all together. Unfortunately FWA is likely to be used for backhaul in more urban areas where the population density justifies the upfront investment.
HAPpy HAPpy, Joy Joy
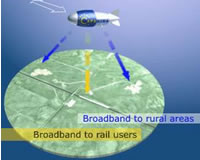
Luckily it looks like there is an answer, and it’s call HAP (High Altitude Platform). There have already been trials of HAP using tethered balloons, and these have been reasonably successful, but there are problems. They are relatively low altitude, so may interfere with other air traffic. However being tethered means they can use the tether cable to connect to the infrastructure on the ground (i.e. say the Internet), but it limits them to being tethered in suitably connected areas.
Utilising a real HAP solution means sending what could be called airships up 20Km or so, these would freely roam the sky. Being so high they wouldn’t interfere with commercial air traffic – of course would still need to get approval from the international aviation authorities, especially for launching them and what happens when something goes wrong or they falls back to earth.
 Other approaches to HAP involve lightweight aircraft, such as the European-funded Capanina project.
Other approaches to HAP involve lightweight aircraft, such as the European-funded Capanina project.
Both balloon and fixed-wing platforms would use radio systems (similar to satellite) to transmit to end-users, who would use a steer able dish that tracks the HAP. Current thoughts are that the HAPs will use both radio and optical transmissions between HAPs (since optical interference is very low at 20Km altitude).
The HAP end-user connection may use existing WiFi-type solutions to actually connect people, so a small village may have a central HAP system which then people connect to using traditional systems.
Where HAP can offer significant benefits, is to moving objects such as trains. They would use a sophisticated electronically steer able aerial to track the HAPs and would allow continuous reception of signals – even between HAPs.
Since the bandwidth between a ground receiver and the HAP would be about 120Mb/s, rural (and moving) users might actually get a better service than traditional broadband users.
Unfortunately it’s going to take a while for this to be a commercial reality, but at least people are thinking about it, trials are commencing now and it’s got European funding.
 With a manly backslap, Intel and Sprint have announced that they will work together to advance development of the 802.16e WiMAX standard.
With a manly backslap, Intel and Sprint have announced that they will work together to advance development of the 802.16e WiMAX standard. In case that sounded too simple, here’s Oliver Valente, CTO and VP of technology development for Sprint, to baffle you with a buzzword remix: “Our relationship with Intel will help validate requirements, drive key ecosystem development needs, formulate network strategies and define the potential for advanced wireless services adoption”.
In case that sounded too simple, here’s Oliver Valente, CTO and VP of technology development for Sprint, to baffle you with a buzzword remix: “Our relationship with Intel will help validate requirements, drive key ecosystem development needs, formulate network strategies and define the potential for advanced wireless services adoption”. Sean Maloney, another executive with an impossibly long job description (“executive vice president and general manager of the Intel Mobility Group”) added: “WiMAX technology has the promise to deliver new broadband services to consumers globally.”
Sean Maloney, another executive with an impossibly long job description (“executive vice president and general manager of the Intel Mobility Group”) added: “WiMAX technology has the promise to deliver new broadband services to consumers globally.” This has Friday Story written all over it. A few Israeli geeks set up a test to compare the speed of delivering data via pigeon (PEI – Pigeon Enabled Internet, as they’ve labelled it) compared with ADSL.
This has Friday Story written all over it. A few Israeli geeks set up a test to compare the speed of delivering data via pigeon (PEI – Pigeon Enabled Internet, as they’ve labelled it) compared with ADSL. As you know, the A in ADSL stands for Asynchronous, so the transferred rates listed equate to the speed that information is received. Upload rates are significantly lower. By their calculations, uploading 4Gb of data on ADSL would take around 96 hours – making the pigeon transfer significantly more efficient, equivalent to a T1 connection at 1.5Mbps.
As you know, the A in ADSL stands for Asynchronous, so the transferred rates listed equate to the speed that information is received. Upload rates are significantly lower. By their calculations, uploading 4Gb of data on ADSL would take around 96 hours – making the pigeon transfer significantly more efficient, equivalent to a T1 connection at 1.5Mbps. Chat around the office lead us to wonder what the next in the endless list of variation on creatures being used to transfer information would be. Nicolas Nova has provided the answer –
Chat around the office lead us to wonder what the next in the endless list of variation on creatures being used to transfer information would be. Nicolas Nova has provided the answer –  BT Rich Media has cuddled up to Sportfive, a French sports marketing group, and announced a partnership to make 2006 Football World Cup qualifying and friendly games available to fans streamed over broadband on the Internet.
BT Rich Media has cuddled up to Sportfive, a French sports marketing group, and announced a partnership to make 2006 Football World Cup qualifying and friendly games available to fans streamed over broadband on the Internet. Football bonkers viewers will be able to choose between 250Kbps or 500Kbps quality streams for approximately £7 (~US$13 ~€10), or alternatively download the entire match to keep forever for around £5 (~US$9.50 ~€7). As a long suffering Wales fan, I have to admit that there’s several games which I never wish to see again!
Football bonkers viewers will be able to choose between 250Kbps or 500Kbps quality streams for approximately £7 (~US$13 ~€10), or alternatively download the entire match to keep forever for around £5 (~US$9.50 ~€7). As a long suffering Wales fan, I have to admit that there’s several games which I never wish to see again! The games will be served up on http://www.qualifiers2006.com and promoted to over 10 million users via a range of affiliate sites such as soccernet.com,.teamtalk.com, sportinglife.com and rivals.net .
The games will be served up on http://www.qualifiers2006.com and promoted to over 10 million users via a range of affiliate sites such as soccernet.com,.teamtalk.com, sportinglife.com and rivals.net . AbbiTalk, a West Sussex-based provider of Voice Over IP (VoIP) telephony services, is talking tough about its cut-rate broadband call packages, that offer customers extra telephone lines with discount local and UK call charges and no line rental.
AbbiTalk, a West Sussex-based provider of Voice Over IP (VoIP) telephony services, is talking tough about its cut-rate broadband call packages, that offer customers extra telephone lines with discount local and UK call charges and no line rental. Prices start at £149 for “AbbiTalkBasicOne”, which provides one extra phone line, a unique number with Pre Pay phone account, an adaptor and a DECT digital cordless phone with digital answering machine.
Prices start at £149 for “AbbiTalkBasicOne”, which provides one extra phone line, a unique number with Pre Pay phone account, an adaptor and a DECT digital cordless phone with digital answering machine. No line rental is charged and there’s no need to use a computer to make the calls as these are accomplished through the standard cordless handsets.
No line rental is charged and there’s no need to use a computer to make the calls as these are accomplished through the standard cordless handsets. The latest National Statistics monthly update to the survey of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) shows that there was a 1.9 per cent increase in the number of active subscriptions to the Internet in the past year (Feb 2004 – Feb 2005)
The latest National Statistics monthly update to the survey of Internet Service Providers (ISPs) shows that there was a 1.9 per cent increase in the number of active subscriptions to the Internet in the past year (Feb 2004 – Feb 2005) Permanent Internet connections rose to 43 per cent of all subscriptions in February 2005 (up 2 per cent from Jan 2005) with a year on year increase of 85.9 per cent for subscriptions for permanent connections.
Permanent Internet connections rose to 43 per cent of all subscriptions in February 2005 (up 2 per cent from Jan 2005) with a year on year increase of 85.9 per cent for subscriptions for permanent connections. Video Networks Limited (VNL), who operate the HomeChoice VOD service around London, have added the children’s animation channel Toonami to their line up using the MPEG-4 / AVC format, making it the world’s first television channel to be encoded with advanced compression technology.
Video Networks Limited (VNL), who operate the HomeChoice VOD service around London, have added the children’s animation channel Toonami to their line up using the MPEG-4 / AVC format, making it the world’s first television channel to be encoded with advanced compression technology. VNL’s migration to MPEG-4 for its remaining broadcast channels, including the Cartoon Network and Boomerang, is expected to be completed within the next two months. In time the VOD service will also be moved to the new CoDec.
VNL’s migration to MPEG-4 for its remaining broadcast channels, including the Cartoon Network and Boomerang, is expected to be completed within the next two months. In time the VOD service will also be moved to the new CoDec. “The first commercially available encoding platform to support MPEG-2, MPEG-4/AVC and SMPTE VC-1, Harmonic’s DiviCom MV 100 enabled VNL to provision a compelling video-over-DSL service while in parallel developing the elements of an MPEG-4 environment.
“The first commercially available encoding platform to support MPEG-2, MPEG-4/AVC and SMPTE VC-1, Harmonic’s DiviCom MV 100 enabled VNL to provision a compelling video-over-DSL service while in parallel developing the elements of an MPEG-4 environment. UK Online is hoping to bring broadband to the masses by smashing the price point for “entry-level” home broadband down to a wallet-untroubling £10 a month.
UK Online is hoping to bring broadband to the masses by smashing the price point for “entry-level” home broadband down to a wallet-untroubling £10 a month. Surfers not used to this level of generosity may be wondering where the catch is, but we haven’t found it yet: we wrote to UK Online and they confirmed that both the Broadband 500 and Broadband 2000 are unlimited services with the Broadband 8000 offering an enormous 500GB monthly download allowance.
Surfers not used to this level of generosity may be wondering where the catch is, but we haven’t found it yet: we wrote to UK Online and they confirmed that both the Broadband 500 and Broadband 2000 are unlimited services with the Broadband 8000 offering an enormous 500GB monthly download allowance. Channel Five yesterday became the first UK broadcaster to launch a legal video download store, offering DVD-quality downloads of some of the most popular features of its flagship car show, Fifth Gear, from its Web site.
Channel Five yesterday became the first UK broadcaster to launch a legal video download store, offering DVD-quality downloads of some of the most popular features of its flagship car show, Fifth Gear, from its Web site. Powering the UK’s first legal video downloads store is a system developed by 7 Digital, the company behind download stores for a raft of leading music companies including Universal and EMI.
Powering the UK’s first legal video downloads store is a system developed by 7 Digital, the company behind download stores for a raft of leading music companies including Universal and EMI. Legal music download sites have become hugely popular in recent years, but TV companies have so far not used the same technology to put programmes online – despite British viewers being the
Legal music download sites have become hugely popular in recent years, but TV companies have so far not used the same technology to put programmes online – despite British viewers being the  DL: Is the site entirely bankrolled by Brewster Kahle (The Internet Archive) or are there plans to raise revenue through advertising/affiliate programs etc?
DL: Is the site entirely bankrolled by Brewster Kahle (The Internet Archive) or are there plans to raise revenue through advertising/affiliate programs etc?