 We covered the announcement of Orange’s 3G TV content to mobile handsets last week, but today we discovered who’s providing the content-to-mobiles technology powering the services.
We covered the announcement of Orange’s 3G TV content to mobile handsets last week, but today we discovered who’s providing the content-to-mobiles technology powering the services.
Idetic, the company behind MobiTV, who are in turn Orange’s partners for the service, are the technical brawn behind the operation. Headquartered in Berkeley, CA they have been around since 1999, originally working on bandwidth optimisation systems for cellular networks.
We spoken extensively with Ray DeRenzo, former Chief Marketing Officer of Vodafone America’s Global Platform and Internet Services Group, who joined Idetic as VP of EMEA (so he’ll have a somewhat less-wide business card these days), running through many areas of their business.
A fortuitous early deal with Siemens saw the creation of a smart proxy server product being bundled with Siemens hardware and begin actively sold, with Siemens effectively becoming a sales agent for Idetic system. This licensing deal gave them the breathing space, and cash flow, to further develop the system.
The roots of the system that is being used on the Orange project lay in a demonstration system for delivering content over IP connections to TV, originally created as a sales tool to sell their optimisation products.
During a demo with a major US broadcaster, the eyes across the table lit up, generating great excitement about using the system to syndicate broadcaster content to many platforms.
This pivotal moment for the company, altered the companies direction, expanding them in a new direction.
 After much careful thinking and planning they’ve ended up with an end-to-end solution, spanning ingestion; digitisation; encoding; and distribution going initially to IP TV, now cellular and wireless.
After much careful thinking and planning they’ve ended up with an end-to-end solution, spanning ingestion; digitisation; encoding; and distribution going initially to IP TV, now cellular and wireless.
In what must have been a pretty big transition for the technical-focused company, they launched MobiTV, hiring the BSD’s from Hollywood, TV and the cellular world. By gathering content distribution deals initially in the US, now Europe and soon Asian markets, they have placed themselves in an enviable position, supplying the delivery system and the content to be delivered – both sides of the transaction.
With expansion into Europe and Asia on their main, back in February, MobiTV swelled their ranks with some of the great and the good from the mobile world, one of which being our interviewee Ray DeRenzo. A smart move bringing in people who’ve been very close to the Giant.
Digital-Lifestyles spoke to Ray this afternoon who confirmed their first trip to MipTV this year had been highly rewarding with many of the content companies beating a path to their door. He commented that seeking content deals has been significantly easier in the US, as the content owners are consolidated into a small number of very powerful providers, differing from the significantly more fractured map of Europe.
Their heritage in the US has done them big favours. The deals that they have made there have enabled them to supply a similar service to the Orange TV service, in the US to Sprint PCS, AT&T Wireless, Cingular Wireless and a number of other regional carriers in the region carrying 23 channels.
These US roots could go someway to clarify why the Orange UK TV service is so weighted towards US content. Signing deals like CNN are a sure thing in many countries of the world.
The simplicity of the whole system is quite beautiful. Ingesting at satellite downlink sites in the US and Europe, this is transferred to their operations centre in the US where the content is prepared and distributed to cellular phone users handsets via their downloaded application. When content is delivered of the handset, the application takes care of the deliver of the content, DRM and rescaling of the video to the specific characteristics of the destination handset.
They’ve opted not to use the RTSP (Real Time Streaming Protocol) standard as many other video streaming services have, but have decided to use their own packeted-delivery approach, which they claim is more bandwidth efficient than leaving the connection constantly open, as RTSP does. It would seem to make sense.
Orange have initially decided to only offer a bundle deal, £10 (~US$18 ~€14.5)per month including 20 hours of access to any of the TV content. MobiTV system is also able to offer many more payment options including one-off payment using micro-payments.
Depending on the handset that is used, MobiTV claim mobile views should be getting a frame rate of around 15 fps, which while it’s around half the frame rate of ‘normal’ TV, sound eminently very watch able – certainly a considerable improvements on the much maligned 1-2 fps of a couple of years ago.
The delivery of TV and video content to the mobile handset is currently white hot both in the content and mobile worlds – and it’s been getting that way for the last 18 months. What has yet to be consistently proven is the consumer’s appetite for paying for it – Will it have the run away success of SMS or only generate the mild interest of MMS.
We don’t know Idetic/MobiTV’s offering intimately, but from the overview we’ve had it certainly looks like an interesting offering.
Idetic
MobiTV
 Frontier Silicon has launched a new module that claims to bring personal-video-recorder (PVR) like capabilities to DAB digital radio.
Frontier Silicon has launched a new module that claims to bring personal-video-recorder (PVR) like capabilities to DAB digital radio. Recordings can be saved onto a memory card on the same radio or played back on any compatible audio unit.
Recordings can be saved onto a memory card on the same radio or played back on any compatible audio unit. Frontier Silicon’s software provides an interface through which EPG and dynamic service information (DLS) can be viewed, with scrolling text allowing information ‘wider’ than the 16-character screen to be seen.
Frontier Silicon’s software provides an interface through which EPG and dynamic service information (DLS) can be viewed, with scrolling text allowing information ‘wider’ than the 16-character screen to be seen. Research from BT shows that the number of users connecting to the Internet via broadband has overtaken dial-up subscriptions for the first time, with 7.4 million broadband customers (including cable) now online.
Research from BT shows that the number of users connecting to the Internet via broadband has overtaken dial-up subscriptions for the first time, with 7.4 million broadband customers (including cable) now online. High speed connections are also good news to those selling goods and services online, with an explosive growth in the consumer market for buying media online, such as films, music and television.
High speed connections are also good news to those selling goods and services online, with an explosive growth in the consumer market for buying media online, such as films, music and television. Two million cable customers now enjoy broadband connectivity through NTL and Telewest.
Two million cable customers now enjoy broadband connectivity through NTL and Telewest. Cardiff vicar Reverend Kimber is hoping that by introducing wireless broadband access from the pews of his city centre church, more people will be encouraged to join his flock at St John’s Church.
Cardiff vicar Reverend Kimber is hoping that by introducing wireless broadband access from the pews of his city centre church, more people will be encouraged to join his flock at St John’s Church. After Kimber approached BT, the company agreed to fill in the gap in Cardiff’s wireless broadband network and fitted the church with its own Openzone node, providing access to surfers sitting in the corner of the north aisle at St John’s.
After Kimber approached BT, the company agreed to fill in the gap in Cardiff’s wireless broadband network and fitted the church with its own Openzone node, providing access to surfers sitting in the corner of the north aisle at St John’s. We covered the announcement of Orange’s 3G TV content to mobile handsets last week, but today we discovered who’s providing the content-to-mobiles technology powering the services.
We covered the announcement of Orange’s 3G TV content to mobile handsets last week, but today we discovered who’s providing the content-to-mobiles technology powering the services. After much careful thinking and planning they’ve ended up with an end-to-end solution, spanning ingestion; digitisation; encoding; and distribution going initially to IP TV, now cellular and wireless.
After much careful thinking and planning they’ve ended up with an end-to-end solution, spanning ingestion; digitisation; encoding; and distribution going initially to IP TV, now cellular and wireless. Like the spotty geek who turns up in the pub with a stunner on his arm, Bluetooth has confounded critics by reaching the significant milestone of five million Bluetooth units shipping per week.
Like the spotty geek who turns up in the pub with a stunner on his arm, Bluetooth has confounded critics by reaching the significant milestone of five million Bluetooth units shipping per week. “When you couple that with the recently announced collaboration between the Bluetooth SIG and UWB,” Foley continued, “Bluetooth technology will further reinforce its leading position far into the future. Even today, we expect this will have a positive impact in Bluetooth uptake.”
“When you couple that with the recently announced collaboration between the Bluetooth SIG and UWB,” Foley continued, “Bluetooth technology will further reinforce its leading position far into the future. Even today, we expect this will have a positive impact in Bluetooth uptake.” Seizing a convenient opportunity to squeeze in a bit of PR, Rosenberg added, “Already today, Nokia has introduced state-of-the-art mobile devices that allow data transmission using both high- speed cellular networks, WLAN hot spot access, and Bluetooth technology.”
Seizing a convenient opportunity to squeeze in a bit of PR, Rosenberg added, “Already today, Nokia has introduced state-of-the-art mobile devices that allow data transmission using both high- speed cellular networks, WLAN hot spot access, and Bluetooth technology.”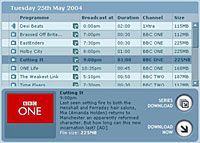 BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming.
BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming. The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.
The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.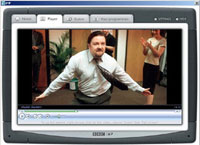 The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc.
The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc. Natalie Mouyal of
Natalie Mouyal of  Generally, countries have tended mix the two strategies. Viewers have benefited from both an increase in the number of television service programmes available, as well as interactive television services. Yet, this combination has not always allowed for an impressive take-off of MHP based interactive services. In the case of Finland, consumers could choose between a zapper set-top box that allows them to access more television service programmes or an MHP-enabled set-top box that allows them to access both the increased number of television services programmes as well as the interactive services. However, MHP-enabled set-top boxes make up only 5% of all set-top boxes currently purchased.
Generally, countries have tended mix the two strategies. Viewers have benefited from both an increase in the number of television service programmes available, as well as interactive television services. Yet, this combination has not always allowed for an impressive take-off of MHP based interactive services. In the case of Finland, consumers could choose between a zapper set-top box that allows them to access more television service programmes or an MHP-enabled set-top box that allows them to access both the increased number of television services programmes as well as the interactive services. However, MHP-enabled set-top boxes make up only 5% of all set-top boxes currently purchased.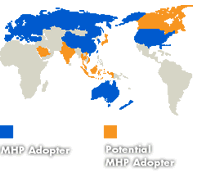 It has been assumed that many consumers will invariably prefer the cheaper zapper set-top box to a more expensive MHP-enabled set-top box. However, this reasoning disregards the type of interactive services offered. For example, should viewers find interactive services compelling and easy to use, they may be willing to spend the extra money necessary for an interactive set-top box. Thus, it would seem that consumer education is key to the successful roll-out of interactive services.
It has been assumed that many consumers will invariably prefer the cheaper zapper set-top box to a more expensive MHP-enabled set-top box. However, this reasoning disregards the type of interactive services offered. For example, should viewers find interactive services compelling and easy to use, they may be willing to spend the extra money necessary for an interactive set-top box. Thus, it would seem that consumer education is key to the successful roll-out of interactive services. NTL Broadcast and O2 have revealed the first batch of channels to be part of their forthcoming mobile TV trial in the Oxford area, announcing an initial 16 channels including Cartoon Network, CNN, Discovery Channel, Sky Sports News and Sky Travel.
NTL Broadcast and O2 have revealed the first batch of channels to be part of their forthcoming mobile TV trial in the Oxford area, announcing an initial 16 channels including Cartoon Network, CNN, Discovery Channel, Sky Sports News and Sky Travel. To support the trial, NTL Broadcast is building a new broadcast network of eight DVB-H transmitters to cover 120 square km around Oxford that will enable the lucky participants to receive digital television on the move. To enable a commercial service to be launched in the UK, Ofcom will need to license spectrum and O2 is already lobbying the UK regulator to bring forward plans to distribute radio frequencies for mobile TV services.
To support the trial, NTL Broadcast is building a new broadcast network of eight DVB-H transmitters to cover 120 square km around Oxford that will enable the lucky participants to receive digital television on the move. To enable a commercial service to be launched in the UK, Ofcom will need to license spectrum and O2 is already lobbying the UK regulator to bring forward plans to distribute radio frequencies for mobile TV services. In Austria, a DTT trial with MHP-based interactive services provided 150 households in Graz with access to an interactive television service called !TV4 using the telephone connection for the return channel. Using their television remote control, viewers could retrieve information services and vote. Given the success of the trial, it is likely that MHP-based interactive services will be launched alongside DTT services.
In Austria, a DTT trial with MHP-based interactive services provided 150 households in Graz with access to an interactive television service called !TV4 using the telephone connection for the return channel. Using their television remote control, viewers could retrieve information services and vote. Given the success of the trial, it is likely that MHP-based interactive services will be launched alongside DTT services. Of course MHP is not the only interactive television service system in the market. Proprietary systems such as MediaHighway and OpenTV have been installed in a large number of set-top boxes, often for cable and satellite platforms. In the United Kingdom, the MHEG standard is widely used on the terrestrial platform. As a result of the various products and services in the market, the DVB Project has been working on the development of the Portable Content Format (PCF) to deliver a wide range of interactive television services to multiple platforms with a minimum of re-authoring. It has significant interest for operators who wish to migrate towards MHP by allowing them to manage simultaneously a mixed population of devices.
Of course MHP is not the only interactive television service system in the market. Proprietary systems such as MediaHighway and OpenTV have been installed in a large number of set-top boxes, often for cable and satellite platforms. In the United Kingdom, the MHEG standard is widely used on the terrestrial platform. As a result of the various products and services in the market, the DVB Project has been working on the development of the Portable Content Format (PCF) to deliver a wide range of interactive television services to multiple platforms with a minimum of re-authoring. It has significant interest for operators who wish to migrate towards MHP by allowing them to manage simultaneously a mixed population of devices. Broadband is taking off everywhere, speeds are increasing and everybody’s happy. Well almost. Broadband isn’t available to all, especially those in more rural areas.
Broadband is taking off everywhere, speeds are increasing and everybody’s happy. Well almost. Broadband isn’t available to all, especially those in more rural areas. Other approaches to HAP involve lightweight aircraft, such as the European-funded Capanina project.
Other approaches to HAP involve lightweight aircraft, such as the European-funded Capanina project.