 The BBC has let rip with a new beta service that invites Web developers and designers outside of the organisation to start fiddling about with their content and “create cool new things”.
The BBC has let rip with a new beta service that invites Web developers and designers outside of the organisation to start fiddling about with their content and “create cool new things”.
Launching in the summer, the BBC Backstage site gives code monkeys, app writers and graphics types the opportunity to bend and twist BBC digital content into new shapes.
The project lets developers get their greasy mitts on a collection of feeds and other tools for “re-mixing” and re-purposing the BBC’s offerings in different ways.
“We want to promote innovation and creativity on the net by opening access to some of BBC’s content and services,” enthused co-project leader Ben Metcalfe.
“Essentially, backstage.bbc.co.uk is enabling developers to create new contexts and user experiences around BBC content, like creating alternative ways to navigate, or remixing it with content and services from other providers like Yahoo,” he continued.
 The UK broadcasting goliath made a commitment to support social innovation in response to last year’s Graf Report, and this is echoed in their plans to develop an open community where people can share expertise, ideas, and collaborative efforts.
The UK broadcasting goliath made a commitment to support social innovation in response to last year’s Graf Report, and this is echoed in their plans to develop an open community where people can share expertise, ideas, and collaborative efforts.
Contributors can join an email discussion and chat away with technical and design staff from the BBC’s new media departments.
The BBC is hoping that by letting creatives fiddle about with their innards, fun, innovative and just plain bonkers new ways of presenting content may emerge, with the possible spin-off of stimulating a UK market for creative venture capital.
By opening up its content feeds and its “API” – application program interface – the BBC hopes that anyone with the right skills can use the digital content to create new search tools, or groovy ways of displaying that content.
An API is essentially a set of computer protocols and tools for building software applications, and the BBC intends to release new APIs gradually, as negotiations with other parts of the BBC take place.
The project is open to just about anyone, and if some bright spark comes up with a particularly cunning idea, the BBC might take it further in collaboration with the developer.
 It’s not all about profit though, with the BBC hoping that contributors will create prototypes on their Web sites to be freely shared with others for non-commercial use.
It’s not all about profit though, with the BBC hoping that contributors will create prototypes on their Web sites to be freely shared with others for non-commercial use.
Users won’t be tied to the BBC either, so if a proposal looks interesting to a third party company, they are free to take them further too.
This approach makes particular sense for applications designed for a specific device – such as a PDA – on which the BBC couldn’t justify dishing out their precious licence fee money.
The beta launch this week is designed to get developers to come up with suggestions about the kind of material they’d like to fiddle about with.
Although it is a significant move for a major content provider like the BBC to publicly offer their APIs, Web big boys like Google and Yahoo have already taken the step of making their APIs available for programmers to create applications.
Opening up material to communities of developers can drive real innovation, although it should be noted that it’s not a free for all, with rules in place detailing what is permitted under the agreement.
“We want to identify online talent and exciting propositions that use that talent and showcase that to the world. We want people to have fun with our content as well,” explained Mr Metcalfe.
BBC Backstage
Graf Report
BBC news cover Backstage
 The BBC has announced a pilot scheme to premiere some new TV programmes before they are broadcast on over traditional channels.
The BBC has announced a pilot scheme to premiere some new TV programmes before they are broadcast on over traditional channels. Jana Bennett, The BBC’s Director of Television, said: “The broadband premiere of The Mighty Boosh is a significant step forward in offering our audiences even greater value in a changing television world.
Jana Bennett, The BBC’s Director of Television, said: “The broadband premiere of The Mighty Boosh is a significant step forward in offering our audiences even greater value in a changing television world. There’s something of a stampede starting up of companies ready and willing to experiment with video over broadband, with BT announcing that it planned to begin trials of video-on-demand (VoD) via broadband early next year, ready for a full commercial roll out scheduled for summer 2006.
There’s something of a stampede starting up of companies ready and willing to experiment with video over broadband, with BT announcing that it planned to begin trials of video-on-demand (VoD) via broadband early next year, ready for a full commercial roll out scheduled for summer 2006. 1. Ofcom have produced more original thinking than I gave them credit for, initially, perhaps because the introduction and summary to the document are not as robust as its contents. Read on…
1. Ofcom have produced more original thinking than I gave them credit for, initially, perhaps because the introduction and summary to the document are not as robust as its contents. Read on… This reflects the EU rules governing the use of State Aid, which require that publicly funded services such as the BBC’s must complement rather than substitute or duplicate provision by the market. Furthermore, where market developments supersede publicly funded provision, the BBC should withdraw from those services or activities and re-direct its valuable public resources to areas of activity where there is a proven market failure. While market failure should not be the only test applied to BBC services, it should provide the underpinning for all publicly funded BBC services. The absence of a market failure analysis raises significant questions as to the compatibility of the BBC’s publicly funded status with European State Aid rules.
This reflects the EU rules governing the use of State Aid, which require that publicly funded services such as the BBC’s must complement rather than substitute or duplicate provision by the market. Furthermore, where market developments supersede publicly funded provision, the BBC should withdraw from those services or activities and re-direct its valuable public resources to areas of activity where there is a proven market failure. While market failure should not be the only test applied to BBC services, it should provide the underpinning for all publicly funded BBC services. The absence of a market failure analysis raises significant questions as to the compatibility of the BBC’s publicly funded status with European State Aid rules.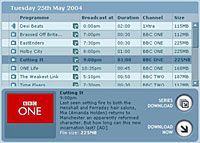 BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming.
BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming. The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.
The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.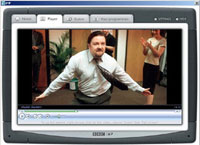 The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc.
The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc. The BBC has let rip with a new beta service that invites Web developers and designers outside of the organisation to start fiddling about with their content and “create cool new things”.
The BBC has let rip with a new beta service that invites Web developers and designers outside of the organisation to start fiddling about with their content and “create cool new things”. The UK broadcasting goliath made a commitment to support social innovation in response to last year’s Graf Report, and this is echoed in their plans to develop an open community where people can share expertise, ideas, and collaborative efforts.
The UK broadcasting goliath made a commitment to support social innovation in response to last year’s Graf Report, and this is echoed in their plans to develop an open community where people can share expertise, ideas, and collaborative efforts. It’s not all about profit though, with the BBC hoping that contributors will create prototypes on their Web sites to be freely shared with others for non-commercial use.
It’s not all about profit though, with the BBC hoping that contributors will create prototypes on their Web sites to be freely shared with others for non-commercial use. The BBC has opened up its RSS news feeds to commercial Websites for the first time, with a new set of terms and conditions letting other sites integrate the BBC feeds for free, and free from offline contractual negotiation.
The BBC has opened up its RSS news feeds to commercial Websites for the first time, with a new set of terms and conditions letting other sites integrate the BBC feeds for free, and free from offline contractual negotiation. Pete Clifton, editor of the BBC News Website said: “Liberating the availability of our content for re-use is an important step for the BBC. We’ve been a bit cautious about it up to now but there’s a real demand for us to provide this service. If we are to build public value it’s important that we respond to this demand.”
Pete Clifton, editor of the BBC News Website said: “Liberating the availability of our content for re-use is an important step for the BBC. We’ve been a bit cautious about it up to now but there’s a real demand for us to provide this service. If we are to build public value it’s important that we respond to this demand.” BBCi has launched a programming service for digital satellite viewers showcasing short films made by ordinary folk across the UK.
BBCi has launched a programming service for digital satellite viewers showcasing short films made by ordinary folk across the UK. Video Nation broke new ground when it first hit UK TV screens – running in short slots dropped in to the programming schedule.
Video Nation broke new ground when it first hit UK TV screens – running in short slots dropped in to the programming schedule. Content on the ‘Your Stories’ service is divided into daily themes, each with its own title. “My Music”, for example, featured an eight-year-old trumpet player and a blind pianist.
Content on the ‘Your Stories’ service is divided into daily themes, each with its own title. “My Music”, for example, featured an eight-year-old trumpet player and a blind pianist. BBCi controller, Rahul Chakkara, explained the reasoning behind Your Stories service: “The BBCi audience is maturing, and is looking for content that is social and highly involving, available to them whenever they want.”
BBCi controller, Rahul Chakkara, explained the reasoning behind Your Stories service: “The BBCi audience is maturing, and is looking for content that is social and highly involving, available to them whenever they want.” BBC Three viewers will be able to schedule their own Sunday night viewing in a pioneering multi-screen application trial starting on 1 May 2005.
BBC Three viewers will be able to schedule their own Sunday night viewing in a pioneering multi-screen application trial starting on 1 May 2005. Emma Somerville, the BBC’s Head of Interactive Programming, added: “Interactive TV can really help our audiences engage with the BBC’s TV channels.”
Emma Somerville, the BBC’s Head of Interactive Programming, added: “Interactive TV can really help our audiences engage with the BBC’s TV channels.” Old school TV listings magazine The Radio Times, has announced a partnership with Gemstar, the Murdoch-owned electronic programme guide (EPG).
Old school TV listings magazine The Radio Times, has announced a partnership with Gemstar, the Murdoch-owned electronic programme guide (EPG). This partnership kicks the Radio Times firmly into the new digital age of television, with the company selling advertising on Guide Plus+ and boosting awareness of the EPG by plugging it relentlessly in its print magazine.
This partnership kicks the Radio Times firmly into the new digital age of television, with the company selling advertising on Guide Plus+ and boosting awareness of the EPG by plugging it relentlessly in its print magazine. Gill Hudson, editor of the Radio Times, declared: “There is now no format not covered by Radio Times – you can access RT via mobile, your PDA, online, and now the Guide Plus+ EPG.”
Gill Hudson, editor of the Radio Times, declared: “There is now no format not covered by Radio Times – you can access RT via mobile, your PDA, online, and now the Guide Plus+ EPG.” British Sky Broadcasting (BSkyB) has announced that it has signed a number of further contracts with technology and equipment suppliers ahead of the forthcoming launch of its High-Definition Television (HDTV) service.
British Sky Broadcasting (BSkyB) has announced that it has signed a number of further contracts with technology and equipment suppliers ahead of the forthcoming launch of its High-Definition Television (HDTV) service. The studio will be fitted out with Tandberg Television HD video head-end with statistical multiplexing with Tandberg EN5990 HD MPEG-4 AVC enabling efficient bandwidth utilisation and high picture quality.
The studio will be fitted out with Tandberg Television HD video head-end with statistical multiplexing with Tandberg EN5990 HD MPEG-4 AVC enabling efficient bandwidth utilisation and high picture quality. HDMI delivers the best possible picture quality to a HD display by maintaining an all-digital connection to DVI equipped displays possible using a suitable adapter cable.
HDMI delivers the best possible picture quality to a HD display by maintaining an all-digital connection to DVI equipped displays possible using a suitable adapter cable. The BBC has moved a step closer to establishing a ‘public domain of audio-visual material’ with the launch of its ‘Creative Archive’.
The BBC has moved a step closer to establishing a ‘public domain of audio-visual material’ with the launch of its ‘Creative Archive’.