 Video Networks Ltd (VNL) has announced that it’s broadband and Video on Demand (VoD) service, HomeChoice, now has 15,000 subscribers, since its relaunch in last September.
Video Networks Ltd (VNL) has announced that it’s broadband and Video on Demand (VoD) service, HomeChoice, now has 15,000 subscribers, since its relaunch in last September.
Eight in ten of their customers have also signed up to the company’s ‘triple play’ package that consists of broadband-delivered TV, broadband and voice calls.
It’s also taking this opportunity to announce that it’s going to be doubling the number of homes it can reach to 2.4 million in London and the Stevenage area, up from 1.2 million.
The VoD component of HomeChoice lets subscribers choose from over 1,000 movies, over 3000 music videos and hundreds of hit TV series, all available to watch exactly when you want.
“The concept of broadband delivered TV and VoD is very new to the entertainment-buying public and to already have 20 per cent market share of new DSL subscribers in our coverage area so soon after our launch is a great achievement. This gives us the confidence to significantly expand our network”, said Roger Lynch, Chairman and CEO VNL Ltd.
VNL initially made inroads into launching its phase 2 footprint in December 2004 when it enabled five new exchanges, including Stevenage – its first exchange outside of the M25. By ‘unbundling’ the exchange, called LLU (Local Loop Unbundling) in the trade, Homechoice is able to provide customers with a 6.5Mbit connection. 2.5Mb are used for TV and VoD delivery, and up to 4Mbit for Internet connection.
The company’s major marketing push for the re-launched HomeChoice service began in September 2004. During Q4 of 2004, VNL was responsible for one in five new DSL net additions in its initial launch footprint of 1.2 million homes.
The company has continued to build on what it offer its subscribers. In August last year, HomeChoice signed a retail deal with BSkyB enabling its subscribers to watch Sky Sports and selected Sky Movies channels on the service. It has also added telephony to its offering, and is about to launch a music download service that will allow HomeChoice customers to buy downloadable music tracks as they appear on screen. It also plans to double the speed of its broadband service from February, at no extra cost: 512Kbps will raise to 1Mb, 1Mbps to 2Mbps, and 2Mbps to 4Mbps.
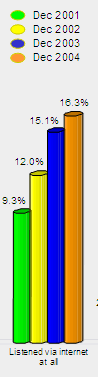 It’s worth clarifying that the Internet figures include any listening of the radio on a computer, whether live streaming, using services like the BBC’s RadioPlayer/Listen Again, or Podcasting (download and play).
It’s worth clarifying that the Internet figures include any listening of the radio on a computer, whether live streaming, using services like the BBC’s RadioPlayer/Listen Again, or Podcasting (download and play). 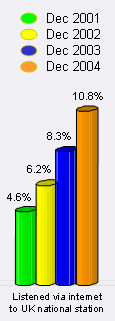 The largest area of growth has been in people listening to UK National radio stations over the Internet. This has increased from 8.3% a year ago to 10.8% of the UK population, equating to just short of 4.8m people. It is thought that this is probably due to an raised awareness that the Internet can be used to listen to the radio, helped in no small part by the BBC pushing the service.
The largest area of growth has been in people listening to UK National radio stations over the Internet. This has increased from 8.3% a year ago to 10.8% of the UK population, equating to just short of 4.8m people. It is thought that this is probably due to an raised awareness that the Internet can be used to listen to the radio, helped in no small part by the BBC pushing the service. 
 Napster, one of the largest players in music downloads, is considering offering a film download service. The new service would sit alongside its music offering and help to give the company a competitive edge over its rivals. The technology is already in place to download movies, so the same service model could easily apply to films, television programmes and video games, now that broadband connection speeds are getting faster and more prevalent.
Napster, one of the largest players in music downloads, is considering offering a film download service. The new service would sit alongside its music offering and help to give the company a competitive edge over its rivals. The technology is already in place to download movies, so the same service model could easily apply to films, television programmes and video games, now that broadband connection speeds are getting faster and more prevalent. Today ntl turned on its much-anticipated Video On Demand (VOD) service in Glasgow.
Today ntl turned on its much-anticipated Video On Demand (VOD) service in Glasgow.  Back at the tail end of last year, Liverpool City Council installed gym equipment with Sony Playstation games consoles fitted to them, in an effort to induce the local youth to come to the gym.
Back at the tail end of last year, Liverpool City Council installed gym equipment with Sony Playstation games consoles fitted to them, in an effort to induce the local youth to come to the gym.  In what isn’t a surprise move Steve Jobs has announced the Apple “Mac Mini”, a low cost addition to the Macintosh computer range. Priced at $499 (~€380, ~£265) and $599 (~€457, ~£319), it can sit in the palm on your hand (measuring 6.5 inches (16.51 cm) square and just 2 inches (5.08 cm) tall and weights just 2.9 pounds (1.32 kg). True to form for Apple, it looks great.
In what isn’t a surprise move Steve Jobs has announced the Apple “Mac Mini”, a low cost addition to the Macintosh computer range. Priced at $499 (~€380, ~£265) and $599 (~€457, ~£319), it can sit in the palm on your hand (measuring 6.5 inches (16.51 cm) square and just 2 inches (5.08 cm) tall and weights just 2.9 pounds (1.32 kg). True to form for Apple, it looks great.