 Toshiba has unveiled its new DVD recorder with the handy ability to set up and record TV programmes via email.
Toshiba has unveiled its new DVD recorder with the handy ability to set up and record TV programmes via email.
The RD-XS54 Multi-Drive (DVD-Ram, DVD-R and DVD-RW) can be connected to other devices over a home Ethernet network.
This means that the RD-XS54 can be connected to a PC, allowing users to share the machine and stream recorded content or live programming to the computer.
With the added connectivity, users can add and edit title information to personal home videos from a PC, upload custom Menu backgrounds for creating DVD-R/RW discs, receive automatic software upgrades and, of course, remotely schedule recordings via email. We like that bit.
The DVD recorder, which ships with a 250GB hard disc drive, also includes a High-Definition Multimedia Interface with “up-conversion” capability to 720p or 1080i.
This conversion will be performed for all sources whether they are playing back content encoded on a DVD or the hard disk, including the tuner and inputs.
“Home networks are rapidly increasing,” said Jodi Sally, vice president of marketing at Toshiba’s America Consumer Products Digital A/V Group.
“With our network-capable DVD recorder we enhance the functionality of the unit. Whether it is being able to schedule a recording via email or by using your home PC to program new recordings, the RD-XS54 makes recording and playback easier and more flexible for consumers”.
The built-in DV input also allows the transfer of camcorder recordings directly onto DVD media, with the unit supporting high speed copying from the HDD to recordable disc, at 12x speed for transferring to DVD-RAM, and 24x for DVD-R.
 The RD-XS54 comes with Toshiba’s EASY NAVI menu and the TV Guide On Screen Interactive Program Guide for simple, easy-peasy channel navigation and recording scheduling.
The RD-XS54 comes with Toshiba’s EASY NAVI menu and the TV Guide On Screen Interactive Program Guide for simple, easy-peasy channel navigation and recording scheduling.
The RD-XS54 has begun shipping in the US with a retail price of US$699.99 (~£385,€570~).
Specs:
Playback compatibility: DVD-Video – CD-Audio – CD-R/RW – SVCD – VCD – DVD-R – DVD-RW – JPEG Picture Disc – WMA – MP3
Record compatibility: DVD-RAM and DVD-R/W
Hard Disc Drive stores up to 250GB Audio and Video
10-Bit / 54Hz Video D/A
Component Video Output: ColorStream Pro Progressive Scan
3:2 Pulldown: Digital Cinema Progressive
181-Channel Tuner
3-D Y/C Comb Filter
Black Level Expansion
3D-DNR Digital Video Noise Reduction Recording
Block and Mosquito DNR Digital Video Noise Reduction Playback
Time Slip Recording / Playback
Pause Live TV / Channel Playback
Time Base Correction
Instant Replay — Instant Skip
VCR Plus+
Inputs: S-Video, Composite, IEEE-1394 (FireWire), RF
Outputs: Component, S-Video, Composite, Optical, RF (Tuner Pass-Through)
Offers HDMI direct digital connection with an HD-ready TV
 A couple of stories have been circulating about the BBC of late, both concerning their adoption of digital TV.
A couple of stories have been circulating about the BBC of late, both concerning their adoption of digital TV. The long-awaited results from the Welsh Digital TV trial were published today.
The long-awaited results from the Welsh Digital TV trial were published today.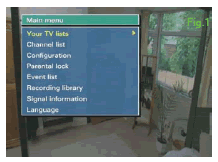 The digital signal was switched on in November 2004, running simultaneously with current analogue for three month.
The digital signal was switched on in November 2004, running simultaneously with current analogue for three month. Transmission and Coverage – No one lost their TV service during the trial. Only three homes, which were previously in poor reception areas, could not receive the digital service and these were given a digital satellite service. Broadband was introduced during the trial and is seen as an alternative form of delivery to satellite.
Transmission and Coverage – No one lost their TV service during the trial. Only three homes, which were previously in poor reception areas, could not receive the digital service and these were given a digital satellite service. Broadband was introduced during the trial and is seen as an alternative form of delivery to satellite. Content – Having an EPG went down well with the residents, particular when they used it to record programs on their PVR. The trialists also enthused about the ability to receive extra TV channels – after all the major benefit to consumer if the expanded choice they will be given.
Content – Having an EPG went down well with the residents, particular when they used it to record programs on their PVR. The trialists also enthused about the ability to receive extra TV channels – after all the major benefit to consumer if the expanded choice they will be given.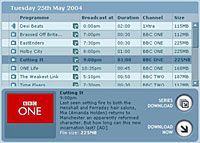 BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming.
BBC New Media is to extend trials of its interactive Media Player (iMP), allowing viewers to download material from 500 hours of its television and radio programming. The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.
The 5,000 trialists will be able to search for programmes they want to watch, filter programmes by channel, select subtitles and, in the case of some series, to collect and watch episodes that they may otherwise have missed.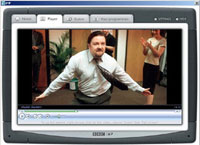 The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc.
The pilot will use DRM software to delete programmes seven days after the programme has aired on TV, ensuring that users can no longer watch the content after that time. The digital rights system will also prevent users emailing the files to their chums or sharing it via disc. Natalie Mouyal of
Natalie Mouyal of  Generally, countries have tended mix the two strategies. Viewers have benefited from both an increase in the number of television service programmes available, as well as interactive television services. Yet, this combination has not always allowed for an impressive take-off of MHP based interactive services. In the case of Finland, consumers could choose between a zapper set-top box that allows them to access more television service programmes or an MHP-enabled set-top box that allows them to access both the increased number of television services programmes as well as the interactive services. However, MHP-enabled set-top boxes make up only 5% of all set-top boxes currently purchased.
Generally, countries have tended mix the two strategies. Viewers have benefited from both an increase in the number of television service programmes available, as well as interactive television services. Yet, this combination has not always allowed for an impressive take-off of MHP based interactive services. In the case of Finland, consumers could choose between a zapper set-top box that allows them to access more television service programmes or an MHP-enabled set-top box that allows them to access both the increased number of television services programmes as well as the interactive services. However, MHP-enabled set-top boxes make up only 5% of all set-top boxes currently purchased.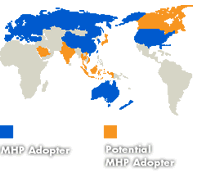 It has been assumed that many consumers will invariably prefer the cheaper zapper set-top box to a more expensive MHP-enabled set-top box. However, this reasoning disregards the type of interactive services offered. For example, should viewers find interactive services compelling and easy to use, they may be willing to spend the extra money necessary for an interactive set-top box. Thus, it would seem that consumer education is key to the successful roll-out of interactive services.
It has been assumed that many consumers will invariably prefer the cheaper zapper set-top box to a more expensive MHP-enabled set-top box. However, this reasoning disregards the type of interactive services offered. For example, should viewers find interactive services compelling and easy to use, they may be willing to spend the extra money necessary for an interactive set-top box. Thus, it would seem that consumer education is key to the successful roll-out of interactive services. In Austria, a DTT trial with MHP-based interactive services provided 150 households in Graz with access to an interactive television service called !TV4 using the telephone connection for the return channel. Using their television remote control, viewers could retrieve information services and vote. Given the success of the trial, it is likely that MHP-based interactive services will be launched alongside DTT services.
In Austria, a DTT trial with MHP-based interactive services provided 150 households in Graz with access to an interactive television service called !TV4 using the telephone connection for the return channel. Using their television remote control, viewers could retrieve information services and vote. Given the success of the trial, it is likely that MHP-based interactive services will be launched alongside DTT services. Of course MHP is not the only interactive television service system in the market. Proprietary systems such as MediaHighway and OpenTV have been installed in a large number of set-top boxes, often for cable and satellite platforms. In the United Kingdom, the MHEG standard is widely used on the terrestrial platform. As a result of the various products and services in the market, the DVB Project has been working on the development of the Portable Content Format (PCF) to deliver a wide range of interactive television services to multiple platforms with a minimum of re-authoring. It has significant interest for operators who wish to migrate towards MHP by allowing them to manage simultaneously a mixed population of devices.
Of course MHP is not the only interactive television service system in the market. Proprietary systems such as MediaHighway and OpenTV have been installed in a large number of set-top boxes, often for cable and satellite platforms. In the United Kingdom, the MHEG standard is widely used on the terrestrial platform. As a result of the various products and services in the market, the DVB Project has been working on the development of the Portable Content Format (PCF) to deliver a wide range of interactive television services to multiple platforms with a minimum of re-authoring. It has significant interest for operators who wish to migrate towards MHP by allowing them to manage simultaneously a mixed population of devices. Today, the US Court of Appeals for the DC Circuit ruled that the US FCC (Federal Communications Commission) does not have authority to prohibit companies from making computer and video hardware that doesn’t comply with the Broadcast Flag. This was to come into effect on 1 July, this year.
Today, the US Court of Appeals for the DC Circuit ruled that the US FCC (Federal Communications Commission) does not have authority to prohibit companies from making computer and video hardware that doesn’t comply with the Broadcast Flag. This was to come into effect on 1 July, this year. We equated it to either a door being slammed, or it being politely pushed closed, but left ajar. It appear as if it’s the big slam.
We equated it to either a door being slammed, or it being politely pushed closed, but left ajar. It appear as if it’s the big slam. As the number of digital TV-enabled households continues to rise and the
As the number of digital TV-enabled households continues to rise and the  The unit’s onscreen interface is simplicity itself, with the eight-day electronic programme guide (EPG) banishing those video timer nightmares forever – this puppy is so simple, even a granny overdosed on Christmas sherry would have no problem setting up a recording of Des and Mel.
The unit’s onscreen interface is simplicity itself, with the eight-day electronic programme guide (EPG) banishing those video timer nightmares forever – this puppy is so simple, even a granny overdosed on Christmas sherry would have no problem setting up a recording of Des and Mel. A range of recording quality modes let you increase recording time at the expense of image quality.
A range of recording quality modes let you increase recording time at the expense of image quality. Highly recommended
Highly recommended BBCi has launched a programming service for digital satellite viewers showcasing short films made by ordinary folk across the UK.
BBCi has launched a programming service for digital satellite viewers showcasing short films made by ordinary folk across the UK. Video Nation broke new ground when it first hit UK TV screens – running in short slots dropped in to the programming schedule.
Video Nation broke new ground when it first hit UK TV screens – running in short slots dropped in to the programming schedule. Content on the ‘Your Stories’ service is divided into daily themes, each with its own title. “My Music”, for example, featured an eight-year-old trumpet player and a blind pianist.
Content on the ‘Your Stories’ service is divided into daily themes, each with its own title. “My Music”, for example, featured an eight-year-old trumpet player and a blind pianist. BBCi controller, Rahul Chakkara, explained the reasoning behind Your Stories service: “The BBCi audience is maturing, and is looking for content that is social and highly involving, available to them whenever they want.”
BBCi controller, Rahul Chakkara, explained the reasoning behind Your Stories service: “The BBCi audience is maturing, and is looking for content that is social and highly involving, available to them whenever they want.” BBC Three viewers will be able to schedule their own Sunday night viewing in a pioneering multi-screen application trial starting on 1 May 2005.
BBC Three viewers will be able to schedule their own Sunday night viewing in a pioneering multi-screen application trial starting on 1 May 2005. Emma Somerville, the BBC’s Head of Interactive Programming, added: “Interactive TV can really help our audiences engage with the BBC’s TV channels.”
Emma Somerville, the BBC’s Head of Interactive Programming, added: “Interactive TV can really help our audiences engage with the BBC’s TV channels.”